Why do single-phase motors use capacitors, but three-phase motors do not need capacitors?
single phase motor
There are two coils in a single-phase motor, the primary coil and the secondary coil. When the single-phase sinusoidal current passes through the main coil, the main coil will generate an alternating pulsating magnetic field. The strength of this magnetic field changes with time as the sinusoidal current changes, but its direction is always in the direction of 1-3.
If there is no force provided by other coils, the motor will not turn after turning 90 degrees. If you want to make it rotate, you must add a force perpendicular to the direction of the main coil, which is provided by the starting coil, that is, the secondary coil.
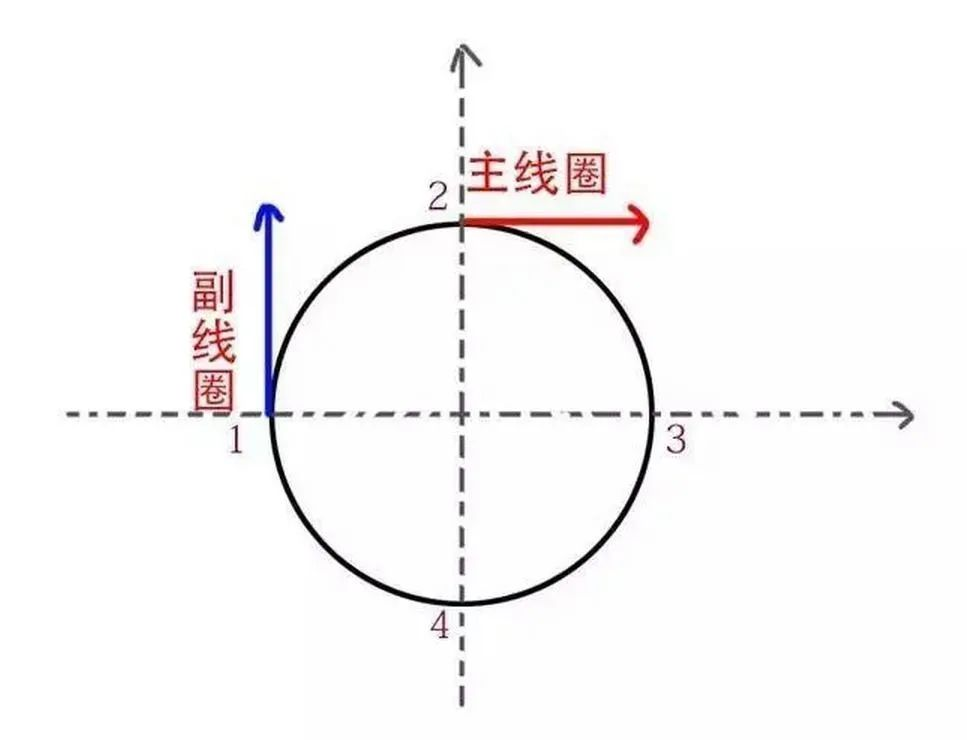
Schematic diagram of the force direction of the single-phase motor coil
In order for the auxiliary coil to provide a force perpendicular to the direction of the main coil, another phase current must be passed to the auxiliary coil. If the same phase current is applied, the direction of their force is also the same. But there is only single-phase electricity, so what should I do?
At this time, it is necessary to use capacitor phase shifting. To put it simply, it is to connect the capacitor in series in the circuit that needs to be phase-shifted, so that the phase of the current changes. After the single-phase alternating current is phase-shifted, its waveform diagram becomes as shown below.
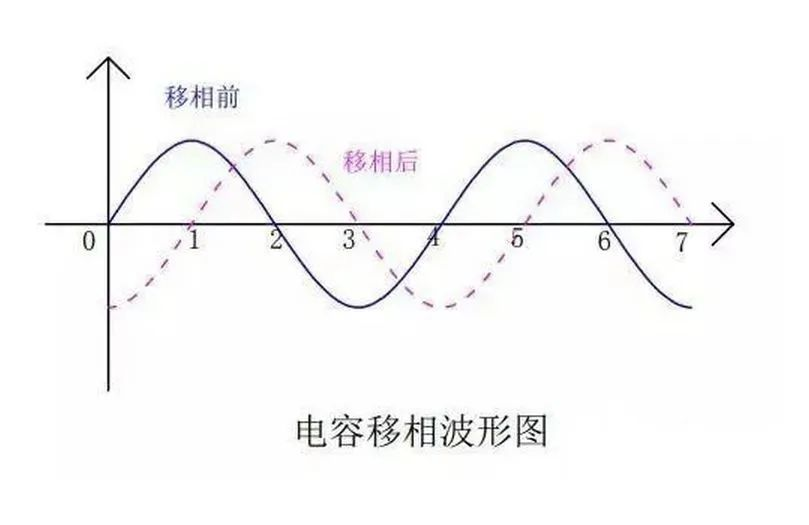
Finally put it together, the motor wiring diagram is as shown below. First, the sinusoidal alternating current comes in from point A, part of it supplies power to the main coil, and the other part shifts the phase through the capacitor. Because the phases of the two-phase electricity are one behind the other, the magnetic field force generated by the coil will also be one behind the other. In this way, the main coil can be pushed, then the secondary coil can be pushed, and finally rotate.
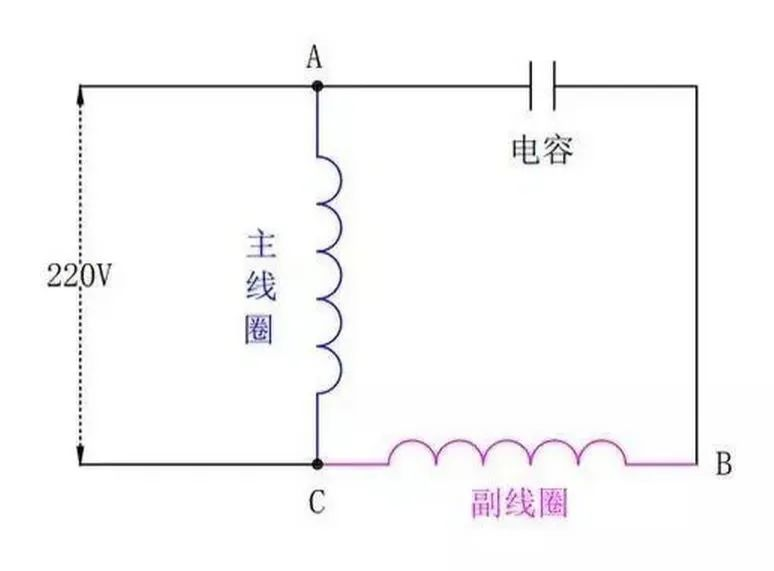
Schematic diagram of single phase motor
If you want the motor to reverse, you only need to change the power cord connected to point A in the above picture to point B, and the power cord connected to point C will not move.
Because before the replacement, the main coil used a sinusoidal alternating current with zero phase, and the secondary coil used a sinusoidal alternating current after phase shifting. After the power line is changed to point B, the secondary coil uses a sinusoidal alternating current with zero phase, while the main coil uses a phase-shifted sinusoidal alternating current. If the current phase of the two coils is changed, the direction of the magnetic force generated by them will also change, and the rotation will also change.
three phase motor
The three-phase motor uses a three-phase AC power supply, and their phase difference is 120° due to the three-phase AC power. When the stator winding is fed with three-phase alternating current, a rotating magnetic field will be generated in the stator. The rotating magnetic field cuts the rotor winding, then the rotor winding will generate an induced current, and the induced current will be subjected to electromagnetic force in the rotating magnetic field, so that it will rotate.
Three-phase motors use three-phase power, and they have a phase difference of 120 degrees. We can simply understand that a three-phase motor is equivalent to three people standing at three different angles to push the rotor. Single-phase motors use single-phase power and capacitors, and the phase difference between the primary and secondary coils is 90 degrees. We can simply understand that a single-phase motor is equivalent to two people standing at two different angles to push the rotor.
Therefore, the torque (rotational force) of a three-phase motor with the same power is greater than that of a single-phase motor.
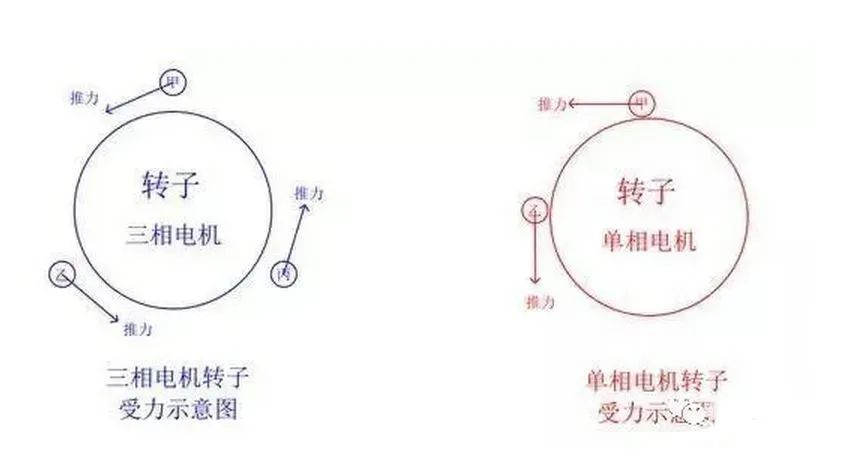
Generally, if there is a three-phase power supply, try to use a three-phase motor, because the three-phase motor with the same power is smaller in size, lighter in weight, lower in noise, lower in price, and higher in torque than a single-phase motor.



























 XINDA
XINDA