Research on off-line detection of commercial vehicle electric drive axle
At present, the common types of electric drive axles for commercial vehicles are mainly divided into wheel-side electric drive axles, parallel-axis electric drive axles and coaxial electric drive axles. As a highly integrated mechatronic drive system, the electric drive axle has many differences from the traditional drive axle, and there is no relevant factory inspection specification in the electric drive axle industry standard. Research work on off-line inspection items and detection methods.
In order to meet the development needs of the new energy vehicle industry, my country has formulated a standard system for pure electric passenger vehicles covering four major areas: basic general purpose, electric vehicle, key systems and components, interfaces and facilities, including key systems and components. The electric drive standard is an important part of the pure electric vehicle standard system. In the past two years, the Society of Automotive Engineers of China has successively released T/CSAE 143-2020 "Specifications for the Evaluation of Pure Electric Passenger Vehicle Integrated Electric Drive Assembly", T/CSAE 176-2021 "Electric Vehicle Electric Drive Assembly Noise Quality Test Evaluation Specification", T/CSAE 143-2020 standard includes test conditions, test requirements, test methods, judgment standards, etc. In terms of commercial vehicles, due to the different layout schemes and structures of the electric drive assembly, a unified testing standard has not yet been formed. People in the industry are still formulating test methods and standards for electric drive axles with reference to individual standards such as motors, reducers, and traditional axles. Technical requirements. In the future, with the highly integrated development of electric drive systems, the layout of electric drive axles will tend to be modularized and platform-based, and the detection methods and requirements for electric drive axles will also become increasingly standardized.
1.1 Single motor standard
At this stage, the standards for single motors are relatively complete, covering the most widely used asynchronous drive motors and permanent magnet synchronous drive motors. Among them, GB/T 18488-2015 "Drive Motor System for Electric Vehicles" stipulates the technical requirements, test instruments, test preparations and various test methods of the drive motor system, and GB/T 29307-2012 "Reliable Drive Motor System for Electric Vehicles" "Reliability Test Method" stipulates the reliability test load specification and reliability evaluation method of the drive motor system on the bench.
1.2 Single standard of reducer
For the new energy vehicle industry, the Automotive Standardization Technical Committee proposed two standards: QC/T 1022-2015 "Technical Conditions for Reducer Assembly for Pure Electric Passenger Vehicles" and QC/T1086-2017 "Technical Conditions for Range Extenders for Electric Vehicles" . Among them, QC/T 1022-2015 stipulates the basic parameters of the reducer assembly, and at the same time puts forward the index requirements for the basic requirements, bench test requirements and cleanliness of the reducer, and stipulates the corresponding test methods.
1.3 Axle single standard
The relevant standards of the current automobile drive axle are: QC/T 533-2020 "Commercial Vehicle Drive Axle Assembly", QC/T 1126-2019 "Terms and Definitions of Automobile Drive Axle", QC/T 293-2019 "Automobile Half-shaft Technology Conditions and Bench Test Methods". Among them, QC/T 533-2020 takes into account more assessment forms and indicators through the integration of axle enterprise standards. The test content and technical requirements such as temperature rise of the axle assembly, lubrication, noise, and fatigue of the inter-wheel differential have further improved the reliability requirements of the axle.
At present, there are mainly ISO, IEC, SAE, JASO and other foreign standard organizations related to automobiles. The standards formulated by these organizations mainly focus on the parts interface and safety test of the whole vehicle. Among them, the automotive engineering academic organization SAE has formulated the drive axle assembly Specifications for components and parts testing and bench test methods. The International Electrotechnical Commission (International Electrotechnical Commission) formulated IEC/TR 60786:1984 "Electric Vehicle Controller", IEC/TR 60785:1984 "Electric Vehicle Rotating Motor" and other electric drive system standards as early as the 1980s . In terms of drive motor testing, the United States has more than 30 testing items, including motor performance, temperature rise, electrical safety and protection functions, environmental adaptability, etc., while Europe and Japan only require maximum power and temperature rise tests.
Before the electric drive axle assembly leaves the factory, in order to ensure the integrity of the product function and no faults, it is necessary to perform functional testing and fault diagnosis at the end of the assembly line. At present, in order to complete the off-line inspection project of the electric drive axle, the industry refers to the test requirements of the national standard test requirements of the drive motor, reducer and traditional drive axle for electric vehicles, and considers the internal structure of the electric drive axle and the working road conditions of the actual vehicle to finally determine the electric drive axle. The main off-line inspection items of the bridge.
3.1 Air tightness test
The air tightness test is to use air, nitrogen or inert gas as the pressurized medium to check whether there is any leakage in the motor cooling circuit and the assembly oil chamber. During the experiment, the temperature of the test medium should be consistent with the temperature of the test environment and kept stable. A vent valve was reserved for the sample, and the pressure was gradually increased to the specified value of the test pressure. After holding the pressure for a certain period of time, the pressure drop value must not exceed the value required by the process. , or in the process of maintaining the pressure, the decrease in the display value of the leak rate instrument should not be greater than the specified value.
3.2 Operation detection
The main purpose of this test is to eliminate the early failure stage of parts through running-in, improve the working surface conditions of each kinematic pair, and verify whether the reducer, differential, shifting and other mechanisms of the electric drive axle can work normally. During the test, the motor speed is increased from zero to the specified speed under no-load or load conditions, and each gear of the test piece is switched in turn. After confirming that there is no abnormality, the high-speed operation of each gear is sequentially detected; the electric drive axle is tested. During differential speed, brake either wheel hub, and the drive motor drives the other wheel hub to double rotation through the transmission system to verify whether the differential can work normally. For specific detection methods, please refer to QC/T 568—2011 "Automobile Mechanical Transmission Assembly Bench Test Method" and QC/T 1022-2015 "Pure Electric Passenger Vehicle Reducer Assembly Technical Specifications" differential gear running-in requirements
3.3 Noise, vibration and roughness detection
During the working process of the axle, any abnormality of any part will cause the axle to generate noise. The traditional detection method of axle operation quality relies on human ears to make subjective judgments on the noise of the axle assembly. It is difficult to quantitatively evaluate the operation status of the axle, and it is easy to cause misjudgment and misjudgment. Noise, Vibration, Harshness (NVH) detection technology can objectively evaluate whether there is abnormal vibration in the running electric drive axle through the decibel meter or vibration sensor, and can effectively prevent defects caused by gears, bearings, etc. The fault caused by the product leaves the factory.
The principle of NVH detection is shown in Figure 1. The NVH detection system mainly analyzes the order vibration signal of the test piece with the help of spectrum analysis method (order and frequency spectrum), and compares it with the tolerance band obtained by manual setting or self-learning, and finds defective products based on the reference value. Among them, self-learning means that the system calculates the envelope curves of the order vibration signals of 100 samples through signal data processing technology during the production process, as shown in Figure 1(a), with the accumulation of test data, the tolerance band It will be continuously optimized, and the NVH detection results will become more accurate and reliable. The order vibration signal interface of the NVH detection system is shown in Figure 1(b). When the order vibration signal exceeds the upper limit of the tolerance band, there is abnormal vibration in the operation of the test piece.
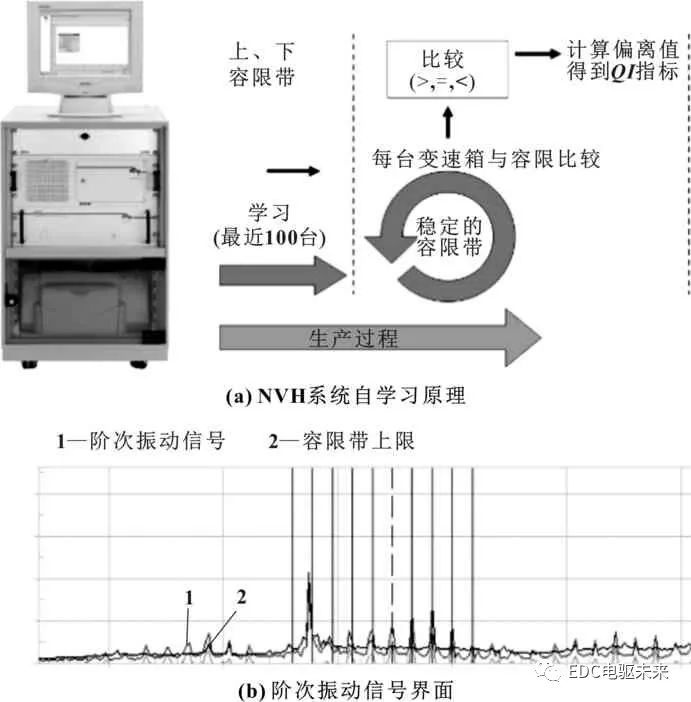
Figure 1 NVH detection principle
3.4 Anti-lock braking system sensor detection
As one of the key components to ensure the safety of driving brakes, the anti-lock braking system (Antilock Braking System, ABS) sensor is installed on the wheel hub of the electric drive axle to detect the wheel speed. The rotational speed data can be used to determine whether the vehicle has a tendency to slip, and make optimal braking adjustments based on the slip ratio. According to GB/T 18459-2001 "Calculation Method of Main Static Performance Indexes of Sensors", the ABS sensor detection items mainly include: maximum induced voltage, minimum induced voltage, and voltage ratio. When the input speed of the drive motor of the electric drive axle is 400 r/min, the measured performance curve of the ABS sensor of an axle within 1 s is shown in Figure 2.
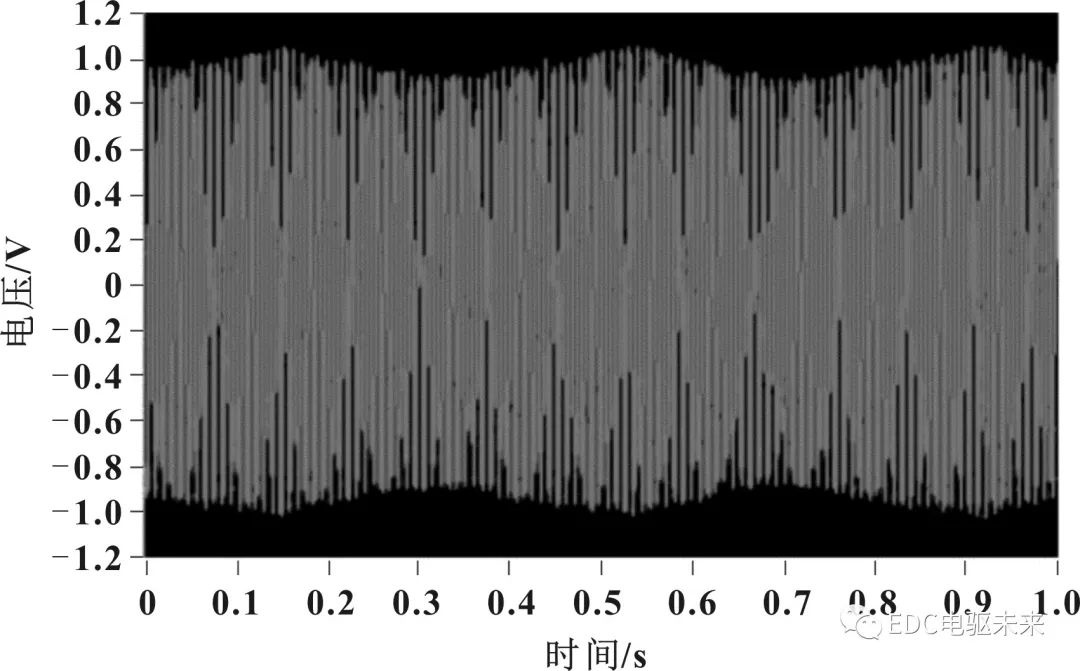
Figure 2 ABS performance test curve
With the development of new energy technology, the standard system of pure electric passenger vehicles has been increasingly improved, and the detection technology of its electric drive axle has also matured. However, the detection and technical requirements of electric drive axles for commercial vehicles have not yet formed a standard specification. This article refers to the inspection standards of motors, reducers, and traditional axles at home and abroad, and combines the technical requirements of the same industry to introduce the off-line inspection of commercial vehicle electric drive axles from four aspects: air tightness, assembly operation, NVH, and ABS sensors. The project and its technical requirements provide a reference for the development of detection systems and quality assessment of similar products.



























 XINDA
XINDA