![]()
MOTOR CUSTOMIZATION | KEY POINTS OF MOTOR CUSTOMIZATION AND COMPARISON OF MOTOR CHARACTERISTICS
1. As a motor manufacturer with a history of 20 years, some customers asked us how to choose a motor and what information we need to provide to make a suitable solution. Looking for Xinda Motor first is the first step to make the right decision.
Our sales staff have accumulated rich experience. Through the following 13 specifications, they can measure your needs like a tailor and tailor a satisfactory motor solution for you.
|
1. Motor usage:
|
|
|
1.1 Small household appliances
|
For example: blender, wall breaker, juicer, hand blender, egg beater, bread machine, food processor, chef machine, pasta machine, soymilk machine, coffee bean grinder, nut sheller, food waste disposal machine, meat slicer, electric knife, air purifier, can opener, knife sharpener, oven, microwave oven.
|
|
1.2 Personal care products:
|
For example: hair dryer, comb, curling iron
|
|
1.3 Vacuum cleaner:
|
For example: dry, wet and dry, rechargeable, vertical, horizontal and portable
|
|
1.4 Garden tools:
|
For example: lawn mower, leaf blower
|
|
1.5 Medical rehabilitation equipment:
|
For example: medical beds, electric wheelchairs, massagers, treadmills, oxygen concentrators
|
|
1.6 Industrial Automation
|
For example: industrial robot
|
|
2. Country:
3. Voltage/frequency:
|
America / Canada
120V/60Hz
|
South America
110V~220V/60Hz
|
Europe
230V/50Hz
|
China
220V/50Hz
|
USA
220V/50Hz
|
Japan
100V/50~60Hz
|
Taiwan, China
110V/60Hz
|
Australia
240V/50Hz
|
|
4. Performance requirements:
|
Power(W)
|
Speed(rpm)
|
Torque(Nm)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5. Dimensions:
|
Shaft extension size
|
Motor outer diameter/total length
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6. Basic structure:
|
Iron sheet/alloy bracket
|
Oil/rolling bearings
|
Plastic/iron fan blades
Centrifugal/axial flow fan blade
|
Single speed/multi speed wiring
|
Single/double steering
|
Electronic brake circuit
|
|
|
|
7. Enameled wire:
|
Stator/rotor pure copper wire
|
Stator pure aluminum wire/
Rotor pure copper wire
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8. Insulation level:
|
Class A (105°C)
|
Class E (120°C)
|
Class B (130°C)
|
Class F (155°C)
|
Class H (180°C)
|
Class N (200°C)
|
|
|
|
9. Protector
|
Protection by coil resistance
|
Temperature Fizz
|
Current Fizz
|
Automatic temperature control switch/
Manual temperature control switch
|
|
|
|
|
|
10. Special parts:
|
Hall assembly, gear, mounting panel, lugs
|
|
11. Special requests :
|
Weight, lifespan, noise, vibration, EMC, FDA, FCC
|
|
12. Project type :
|
Brand new development
|
Modify on the original basis
|
Keep the original design unchanged and replace the original supplier
|
|
13. Estimated annual usage:
|
50K, 100K, 500K, 1000K, above 1000K
|
2. Motor selection is a big question. If you choose the right one, the performance and price of the motor will be reasonable. If you choose the wrong one, you will spend money on something that is not what you want. Therefore, we have compared the three main categories of motors in a simple way for everyone. Capacity is easy to understand.
Motor type pictures:
|
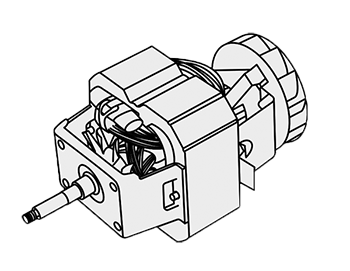
AC series motor
|
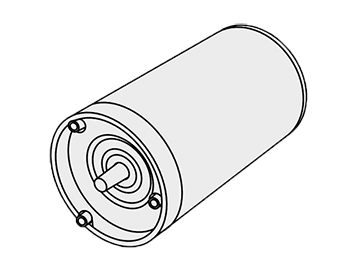
Permanent magnet DC motor
|
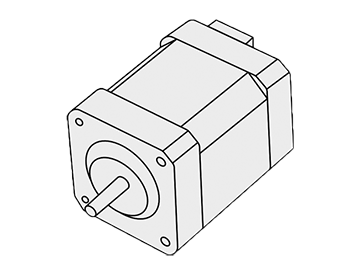
Brushless DC motor
|
2.1 Comparison of no-load motor characteristics
|
Motor type
|
No load
|
|
input power
|
efficiency
|
Rotating speed
|
Torque
|
|
AC series motor (PU6330)
|
middle
|
middle
|
high
|
Low
|
|
Permanent magnet DC motor (PT2745)
|
Low
|
middle
|
middle
|
Low
|
|
Brushless DC motor (PBL6525)
|
high
|
Low
|
middle
|
Low
|
From
From the above no-load state, the speed of the AC series pole motor is relatively high. Those who have requirements for noise should pay special attention to it. Those who need to start from a low speed without load can choose a permanent magnet DC motor. In other aspects, it is not worth comparing at no load. .
2.2 Comparison of motor characteristics at maximum efficiency:
|
Motor type
|
Maximum efficiency
|
|
input power
|
efficiency
|
Rotating speed
|
Torque
|
|
AC series motor (PU6330)
|
middle
|
middle
|
middle
|
middle
|
Permanent magnet DC motor (PT2745)
|
middle
|
middle
|
middle
|
middle
|
|
Brushless DC motor (PBL6525)
|
high
|
high
|
middle
|
high
|
From the above maximum efficiency point, AC series-pole motors and permanent magnet DC motors perform equally well, and their costs are similar. However, permanent magnet DC motors require an AC-to-DC rectifier in the power supply, and the cost increases slightly.
Since the permanent magnet DC motor uses a DC power supply, the effective value of the input power is larger than that of the AC series-pole motor, so it is relatively stable when used with a load and has less speed reduction than when it is loaded.
The performance of brushless DC motors is particularly powerful and is very superior at the load point, but it needs to be considered that the cost of brushed DC motors is more than 10 times higher. This is why the retail price of finished products using brushless DC motors is more than a thousand yuan.
2.3 Comparison of motor characteristics at maximum output power
|
Motor type
|
Maximum output power
|
|
input power
|
efficiency
|
Rotating speed
|
Torque
|
|
AC series motor (PU6330)
|
high
|
llow
|
Low
|
middle
|
|
Permanent magnet DC motor (PT2745)
|
Low
|
middle
|
high
|
Low
|
|
Brushless DC motor (PBL6525)
|
very high
|
high
|
high
|
high
|
At maximum output power, both AC series pole motors and permanent magnet DC motors are not recommended for use at this load point, while brushless DC motors still perform strongly. The only consideration is cost.
For traditional products, because price is the key point to attract users, brushless DC motors are not very versatile at present. However, through the miniaturization, speed and lightweight of brushless DC motors, the product experience has been improved.
In addition, it is easy to cooperate with electronic control to produce variable performance, and the life of the motor is no longer limited by carbon brushes, so it is often used in high-end products.






























 XINDA
XINDA