Graphical analysis of 8 kinds of motor coil failure reasons, intuitive and practical!
When the motor is under abnormal working conditions (including electrical, mechanical and environmental aspects, etc.), the life of the motor coil will be severely reduced. The reasons for the failure of the fan coil are: phase loss, short circuit, coil grounding, overload, rotor lock, voltage imbalance, and power surge . The following are pictures of various coil failures, which can help you correctly identify the cause of failure (take a 4-pole motor as an example).
1. New coil picture

2. Phase loss
A phase loss is an open circuit of one phase of the power supply. The main reason is that the fuse of one phase is blown, the contactor is opened, or the power line of one phase is broken.
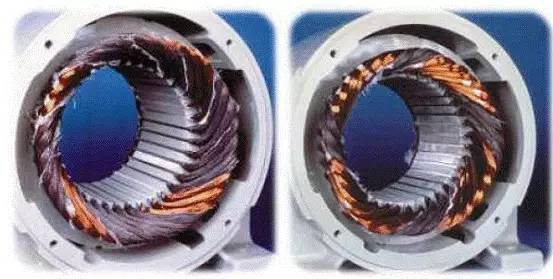
Star connection (Y connection) Delta connection
The picture above is a picture of a 4-pole motor with a lack of phase and burnt out. If the motor coil is burned out symmetrically, it is burnt out due to a lack of phase. A group of coils is good; if the triangular connection is fired with a lack of phase, a 2-pole motor will burn 2 sets of coils symmetrically, and a 4-pole motor will burn 4 sets of coils symmetrically.
3. Short circuit
The following pictures illustrate motor failures caused by contaminants, wear, vibration, etc.
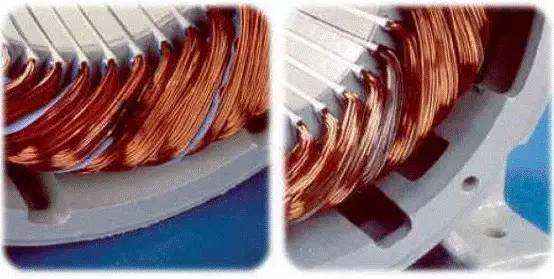
Phase-to-phase short circuit Turn-to-turn short circuit
4. Coil grounding
The following pictures illustrate motor failures caused by contaminants, wear, vibration, etc.

Motor slot breakdown Slot breakdown
5. Overload
Motor overload use will cause motor overload.
Note: Both undervoltage and overvoltage will cause insulation damage and cause overload.

6. The rotor is locked
This situation will cause the motor to heat up a lot, which is probably caused by frequent starting or reverse rotation of the motor.

7. Uneven three-phase voltage
Uneven voltage will cause insulation damage, which may be caused by unstable power supply and poor wiring.
NOTE: A 1 percent voltage imbalance can result in a 6 to 10 percent current imbalance.

8. Surge
The situation shown in the figure below is generally caused by a power surge. Surges may be caused by electrical equipment such as power grids, lightning, capacitors, etc.



























 XINDA
XINDA