![]()
Many engineers have not figured out for a long time what is the difference between a brushless motor and a brushed motor? What is the difference between a synchronous motor and an asynchronous motor? Are all servo motors AC motors? Are all servo motors synchronous motors? Are stepper motors DC motors or AC motors? Does the steering gear belong to the servo motor and so on...
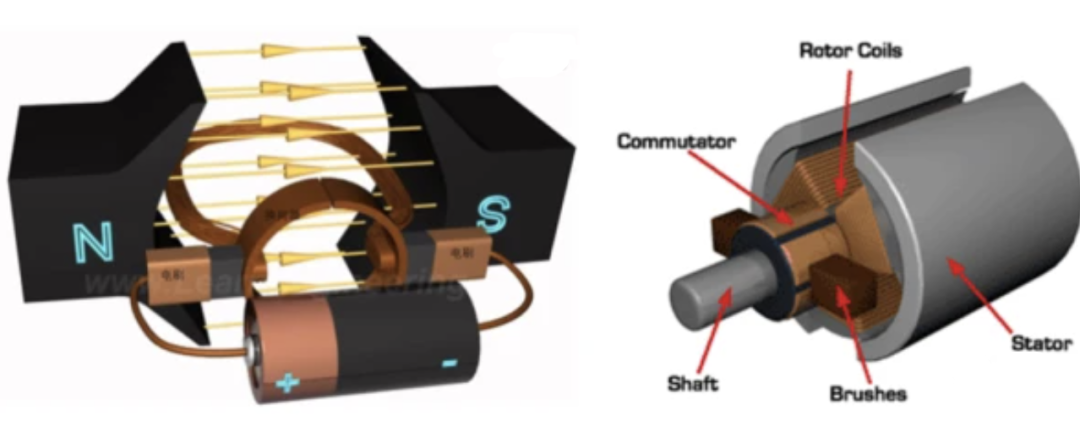
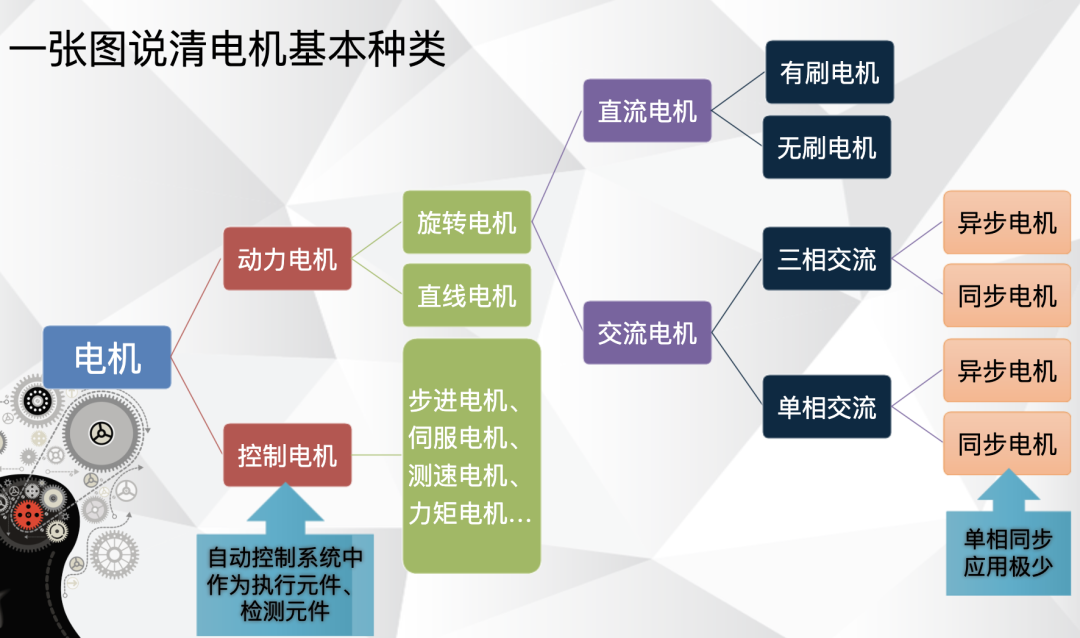
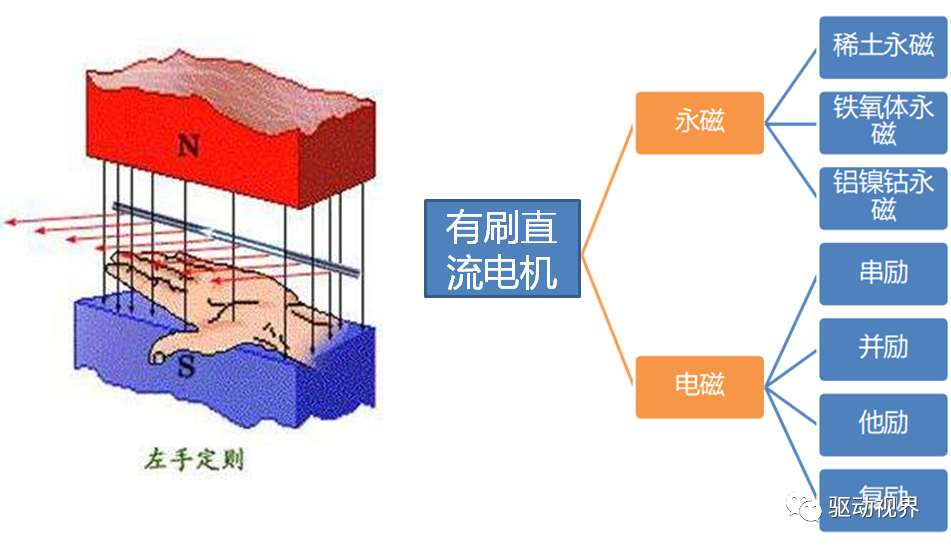
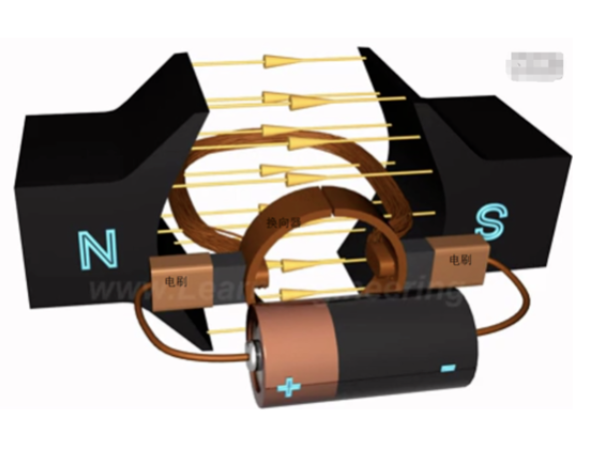
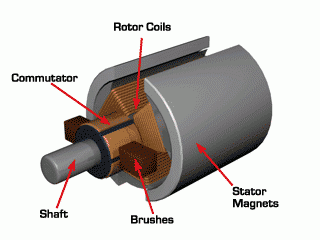
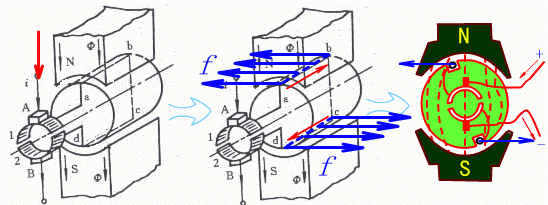
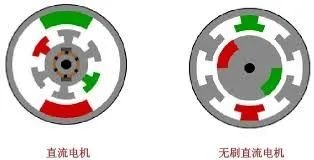
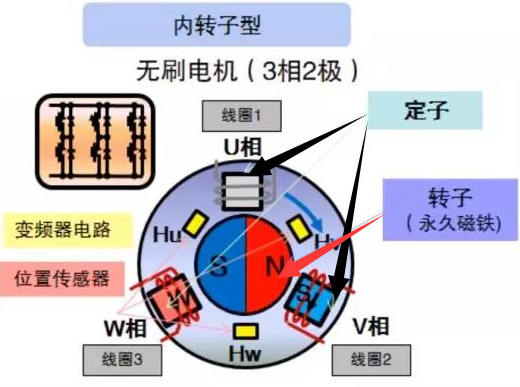
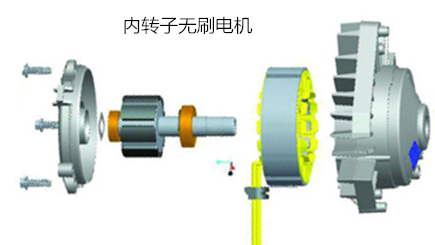
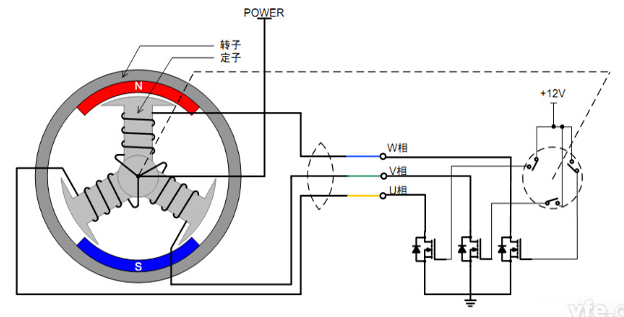
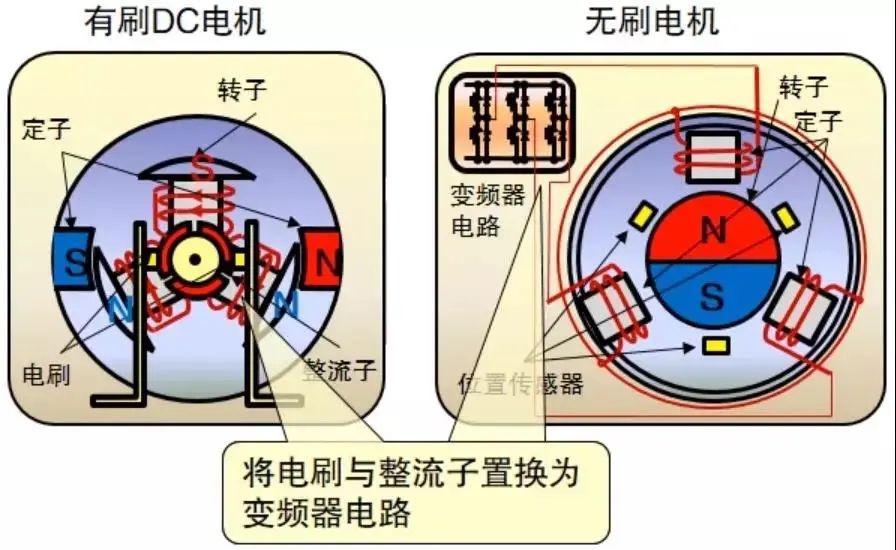
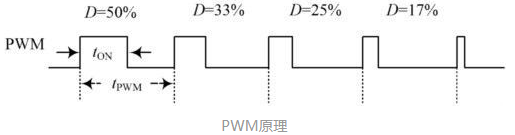
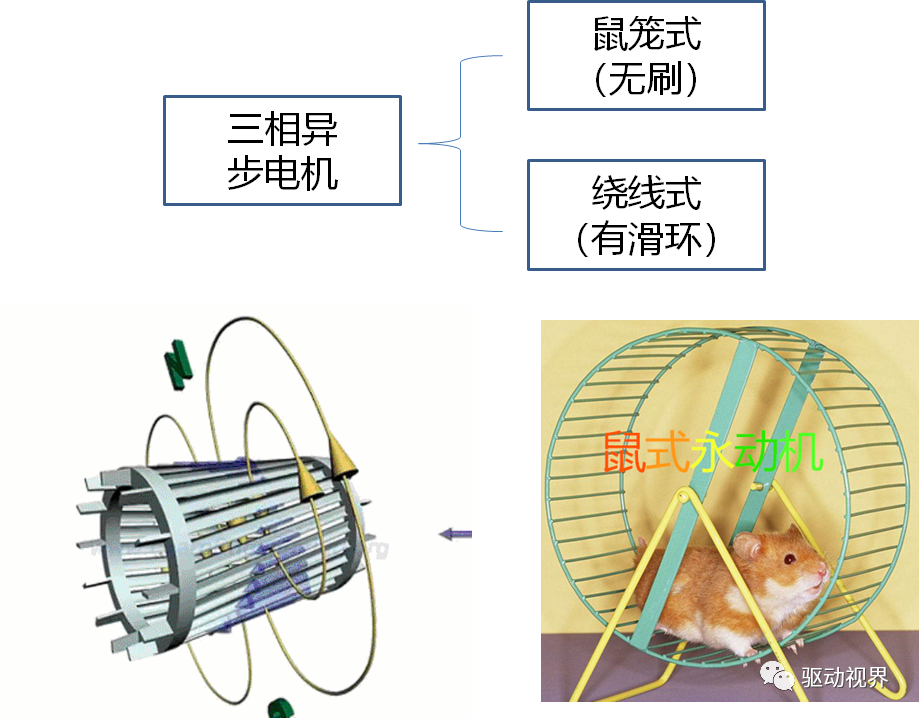
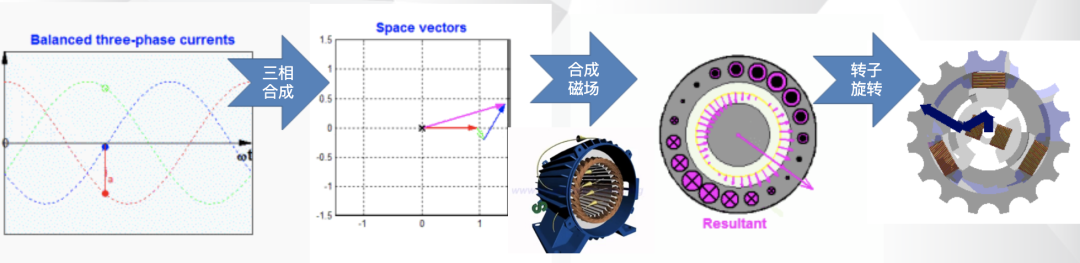
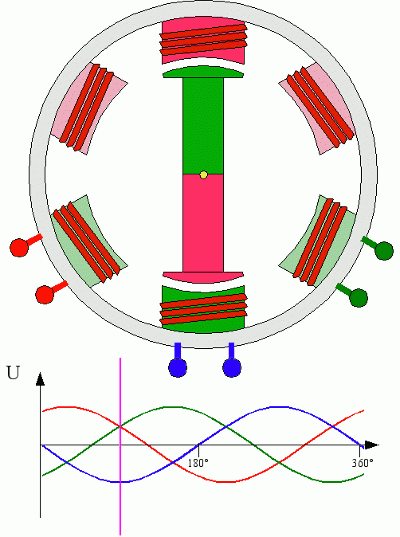
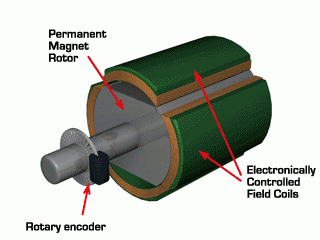
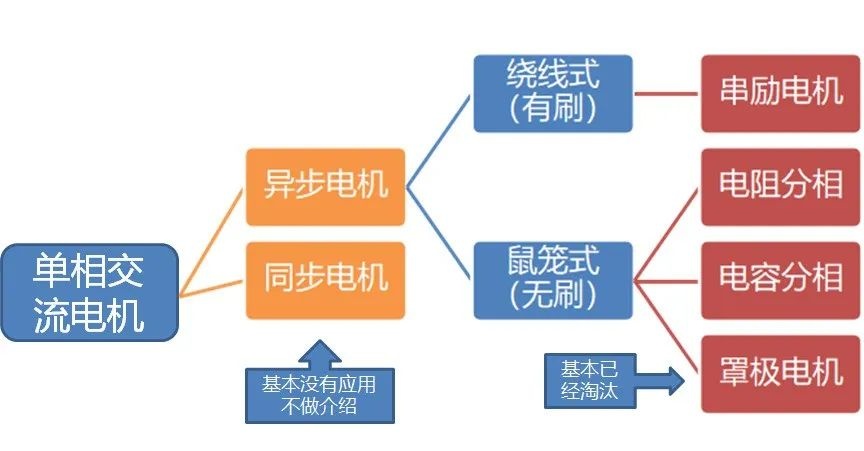
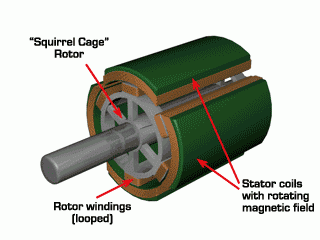
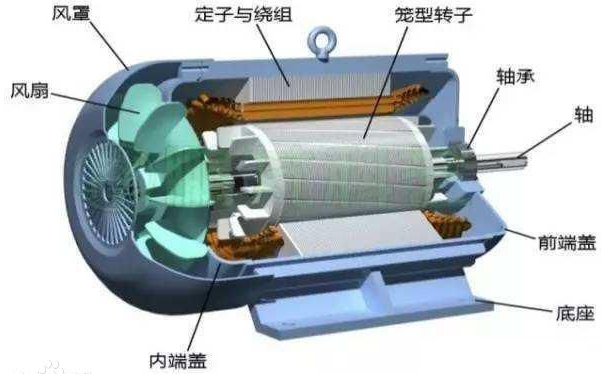
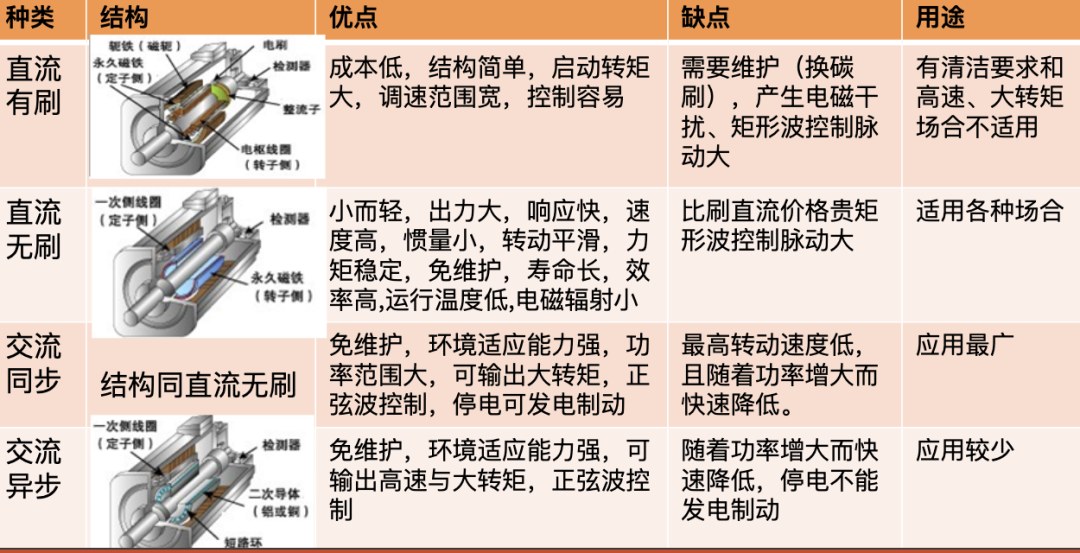
Do you also have a lot of doubts about this? This article will try to explain systematic knowledge in plain language, and I hope that after reading it, you will have a clear understanding of the classification of motors.Those who have studied physics in middle school know that in order to study the force of the current-carrying conductor in the magnetic field, we practiced the left hand into a broken palm, which is exactly the principle of the DC motor.All motors are composed of a stator and a rotor. In a DC motor, in order to make the rotor turn, the direction of the current needs to be constantly changed, otherwise the rotor can only turn half a circle, which is like a bicycle pedal.So a DC motor needs a commutator.Generalized DC motors include brushed motors and brushless motors.The brushed motor is also called a DC motor or a carbon brush motor. The DC motor that is often said refers to a brushed DC motor. It adopts mechanical commutation, the external magnetic pole does not move, and the internal coil (armature) moves, and the commutator and rotor coil rotate together. , the brushes and magnets do not move, so the commutator and the brushes rub against each other to complete the switching of the current direction.Disadvantages of brushed motors:1. The sparks generated by mechanical commutation cause commutator and brush friction, electromagnetic interference, high noise and short life.2. The reliability is poor, there are many failures, and frequent maintenance is required.3. Due to the existence of the commutator, the inertia of the rotor is limited, the maximum speed is limited, and the dynamic performance is affected.Since it has so many shortcomings, why is it still widely used, because it has high torque, simple structure and easy maintenance (that is, carbon brush replacement), and is cheap.DC Motor - Brushless MotorBrushless motor is also called DC variable frequency motor (BLDC) in some fields. It adopts electronic commutation (Hall sensor), and the coil (armature) does not move, and the permanent magnet can be outside the coil or inside the coil. , So there are outer rotor brushless motors and inner rotor brushless motors.Brushless motors are constructed in the same way as permanent magnet synchronous motors.However, a single brushless motor is not a complete power system, and the brushless motor must be controlled by a brushless controller, that is, an ESC, to achieve continuous operation.What really determines its performance is the brushless electronic speed controller (that is, the ESC).Generally, there are two types of drive current for brushless motors, one is square wave and the other is sine wave.Sometimes the former is called a DC brushless motor, and the latter is called an AC servo motor, which is exactly a type of AC servo motor. (video portal)Brushless motors operate in different ways, and can be divided into inner rotor brushless motors and outer rotor brushless motors.The inner rotors are all three-phase, and the price is more expensive.The outer rotor is usually single-phase, the price is close to the people, and the mass production is close to the carbon brush motor, so it has been widely used in recent years.The price of the three phases of the outer rotor is already close to the price of the inner rotor. Well, as you can guess, the disadvantages of brushed motors are the advantages of brushless motors.It has the advantages of high efficiency, low energy consumption, low noise, long life, high reliability, servo control, stepless frequency conversion speed regulation (up to very high speed), etc. It is much smaller than the brushed DC motor, The control is simpler than the asynchronous AC motor, and the starting torque is large and the overload capacity is strong. As for the disadvantages...it is more expensive than the brushed one, and it is not easy to maintain.DC motor - speed regulation principleSpeed regulation of DC motor: The so-called speed regulation means to obtain the required torque by adjusting the motor speed.DC (brush) motors can adjust the speed by adjusting the voltage, connecting resistors in series, and changing the excitation. However, it is the most convenient and commonly used to adjust the voltage. At present, PWM is mainly used for speed adjustment. PWM is actually to realize DC through high-speed switches. Voltage regulation, within a cycle, the average voltage will be high if the on time is long, and the average voltage will be low if the off time is long. .However, the brushes and commutator wear out for a long time, and at the same time, there is a huge current change when commutating, which is very easy to generate sparks. The commutator and brushes limit the capacity and speed of the DC motor, making the speed regulation of the DC motor encounter difficulties. bottleneck.For brushless DC motors, only the input voltage is controlled on the surface during speed regulation, but the self-controlled frequency conversion speed regulation system of the motor (the brushless DC motor itself has a rotor position signal acquisition device such as a rotor position detector, and the rotor using this device The position signal is used to control the commutation time of the variable voltage variable frequency speed control device) and the frequency is automatically controlled according to the variable voltage. It is almost the same as a DC (brush) motor, which is very convenient.Since the rotor adopts permanent magnets, no special excitation winding is required. Under the same capacity, the motor is smaller in size, lighter in weight, higher in efficiency, more compact in structure, more reliable in operation, and better in dynamic performance. Drivers and other aspects have been widely used.Three-phase AC motor - asynchronous motorAC motors are divided into synchronous motors and asynchronous motors. Synchronous motors are mostly used for generators, and asynchronous motors are mostly used for motors.The shell of the motor is the stator, and there are three-phase symmetrical AC windings on the stator. Due to the sequence change of the three-phase electricity, a rotating synthetic magnetic field is formed, and the rotation speed of the magnetic field is the synchronous speed.Synchronous speed n=60f/p, f is the frequency, p is the number of pole pairs, for example, for a 2-pole motor connected to the national grid at 50Hz (that is, the number of pole pairs is 1 pair), then the speed n=60*50/1=3000r /min.Similarly, the synchronous speed of 4-pole, 6-pole and 8-pole motors is 1500, 1000, 750.The asynchronous motor mechanism is simple, and the rotor is a closed coil, such as a squirrel cage.The rotor coil will cut the rotating magnetic field, generate induced electromotive force, and then generate induced current, and finally generate a rotating magnetic field, so that the rotor becomes an electromagnet, which will rotate with the stator magnetic field, so the speed of the rotor must be less than the rotating magnetic field of the stator, so that Cut the lines of flux.That is, the asynchronous speed of the rotor is less than the synchronous speed, and there is a speed difference between the rotor and the stator magnetic field, so it is called an asynchronous motor.The rated speed of asynchronous motors produced by different manufacturers is slightly different. The 2-pole motor is about 2800+r/min, and the 4-pole, 6-pole, and 8-pole asynchronous motors are about 1400+, 950+, and 700+.The speed of the asynchronous motor is high when it is unloaded, and the speed decreases when it is loaded.The asynchronous motor has simple structure, convenient maintenance, reliable operation and low price, and is widely used.Three-phase AC motor - synchronous motorIf the rotor speed = the rotation speed of the stator magnetic field, it becomes a synchronous motor. At this time, the stator needs to be turned into an electromagnet or a permanent magnet, that is, the stator is energized. At this time, it can rotate without cutting the magnetic field line. The speed is the same as the magnetic field rotation speed, that is, a synchronous motor is formed. The rotor structure of synchronous motor is more complicated than that of asynchronous motor, and the price is higher. It is not as widely used in production and life as asynchronous motor. It is mainly used as a generator. Now thermal power stations, hydropower stations, steam turbines, and water turbines are basically synchronous motors.Three-phase AC motor - speed regulation of asynchronous motor
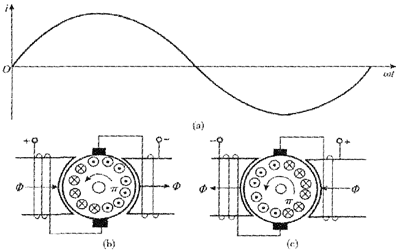
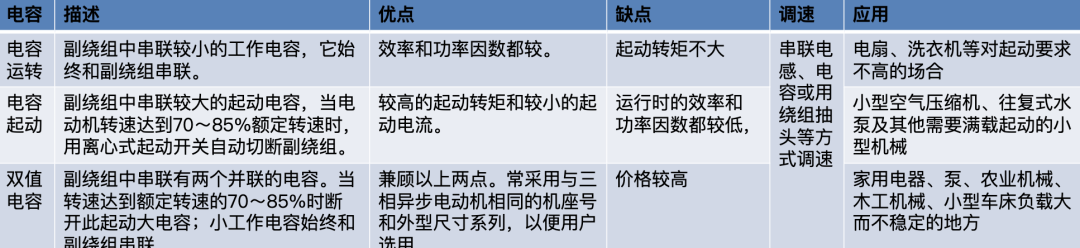
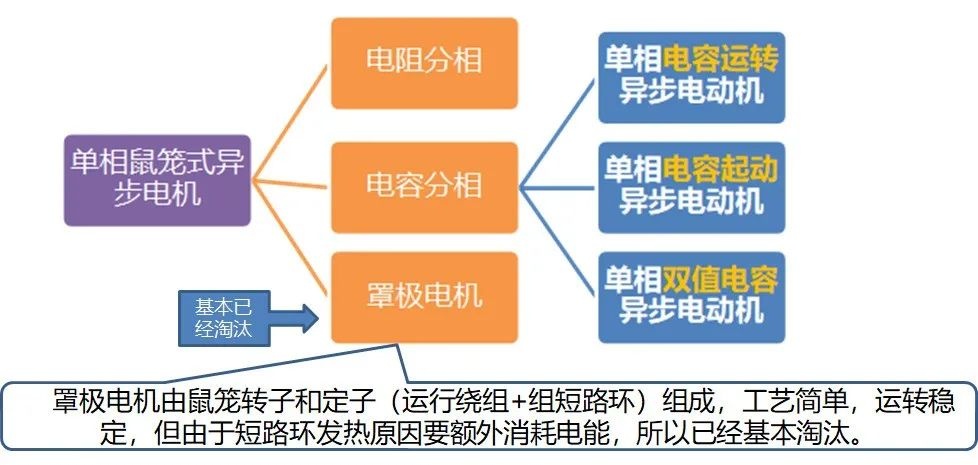
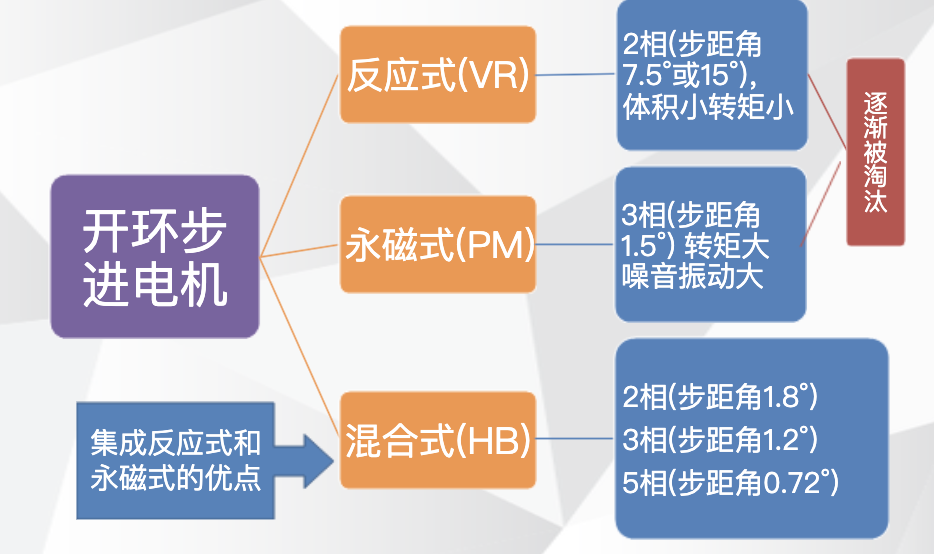
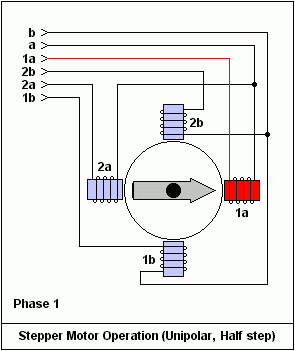
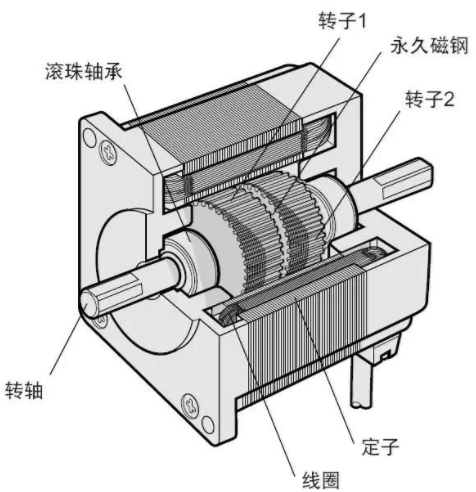
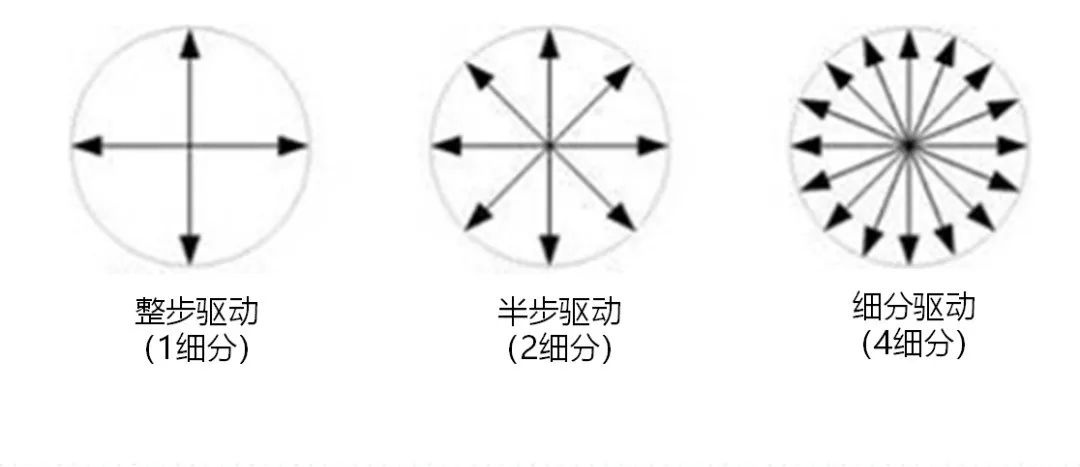
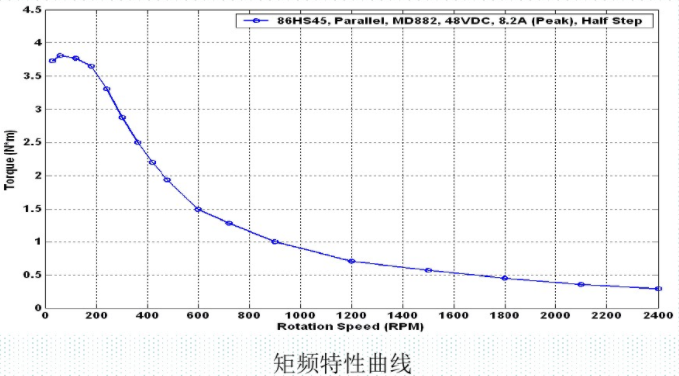
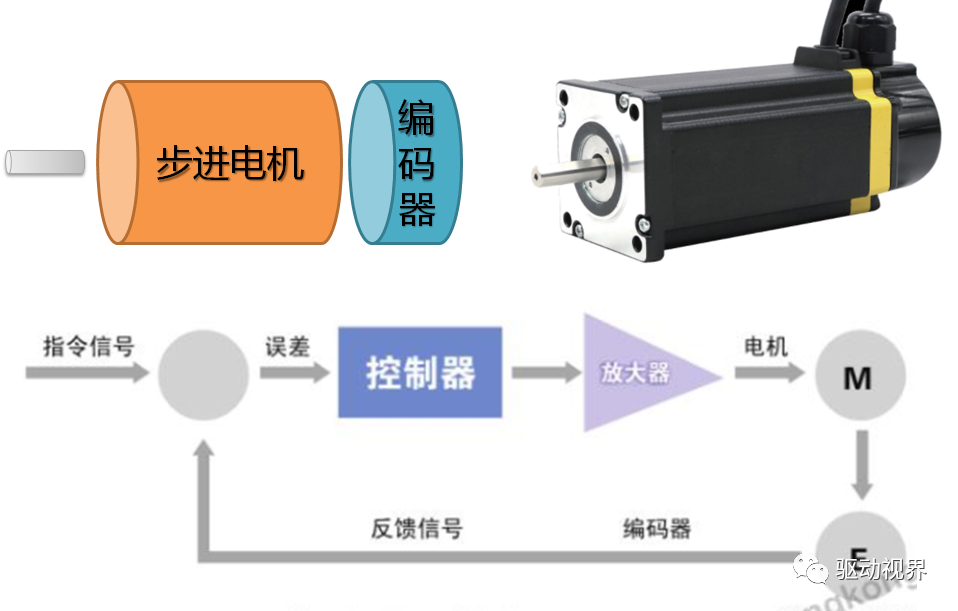
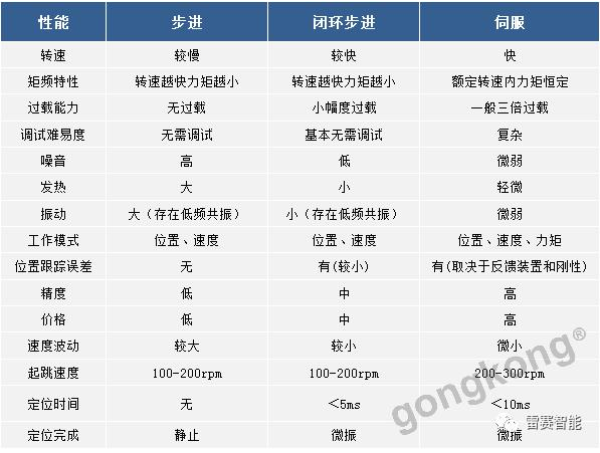
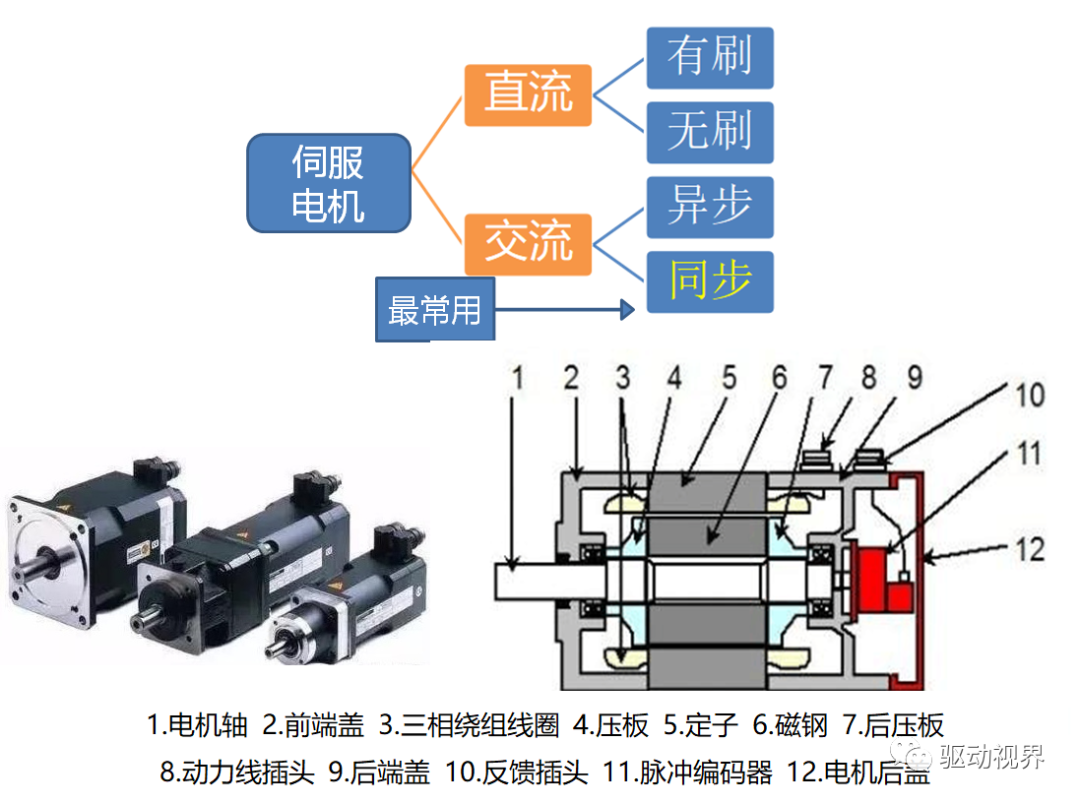
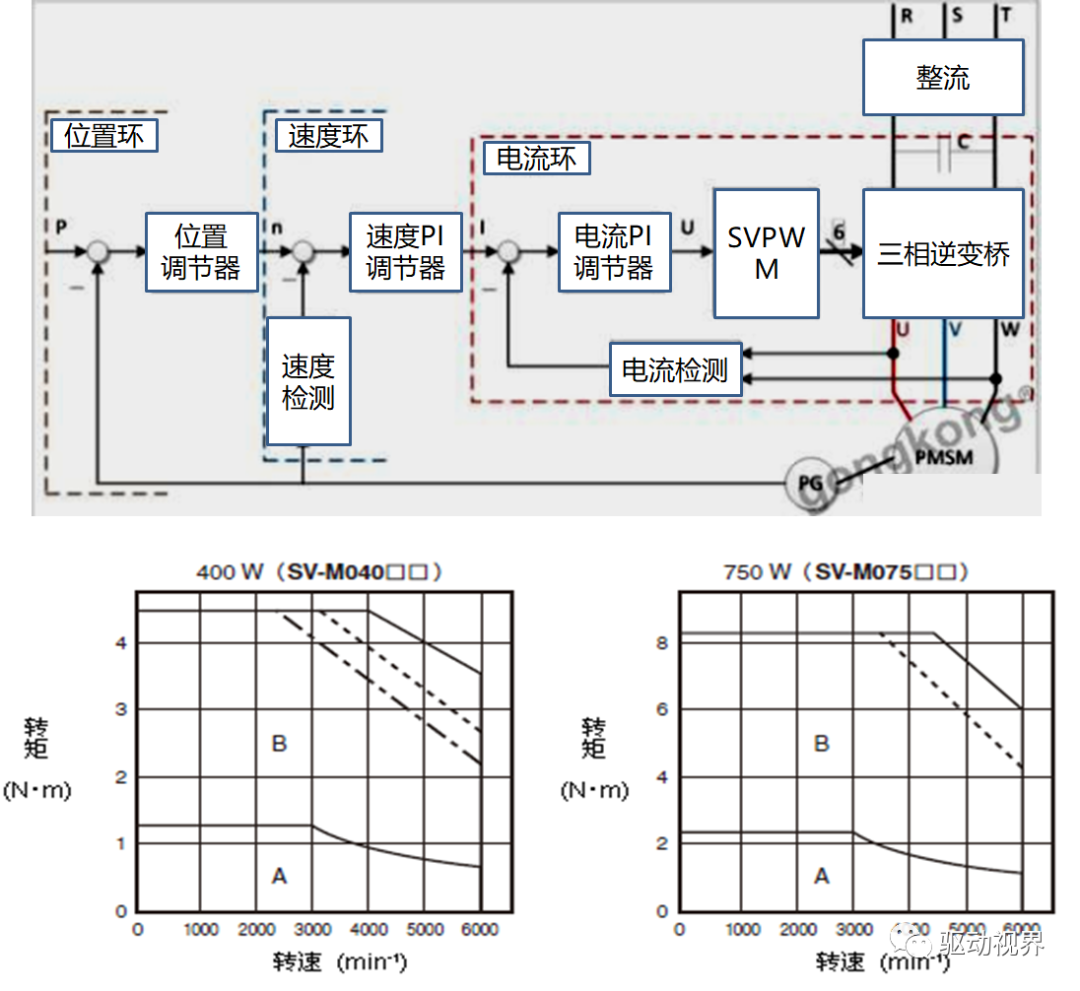
Speed regulation of asynchronous motor: In theory, asynchronous motor can control AC frequency, voltage, or rotor resistance, and motor magnetic pole distribution can be adjusted, but in fact, stepless speed regulation can be realized by adjusting frequency and voltage.Due to the small range of voltage regulation and speed regulation, it can only be used in occasions where the speed regulation is not high, and the application is not extensive. Frequency conversion speed regulation: When it comes to frequency conversion, everyone may have heard of it.The full name of variable frequency speed regulation is variable voltage variable frequency speed regulation (VVVF), that is, the voltage is changed when the frequency is changed, so that the speed regulation range of the asynchronous motor is large enough.Frequency converters can be divided into two categories: AC-AC frequency conversion and AC-DC-AC frequency conversion.AC-AC frequency conversion: The AC power is directly converted into another frequency AC power through power electronic devices. The maximum output frequency cannot exceed half of the input frequency, so it is generally only used in low-speed, large-capacity systems, which can save huge gears Gearbox.The AC-DC-AC inverter rectifies the AC power into DC first, and then converts it into an AC with controllable frequency and voltage through the inverter. With the PWM technology, this inverter can realize a wide range of variable voltage and frequency.For electric vehicles, the asynchronous motor is durable, has a strong overload capacity, and the control algorithm is so mature that it can be used.Three-phase AC motor - speed regulation of synchronous motorSpeed regulation of synchronous motors: Synchronous motors have no slip rate. In the case of a certain structure, the control voltage cannot change the speed. Therefore, before the appearance of frequency converters, synchronous motors cannot be adjusted at all.The emergence of frequency converters has given AC synchronous motors a huge range of speed regulation. Because the rotor also has independent excitation (permanent magnets or electric excitation), its speed regulation range is wider than that of asynchronous motors, and synchronous motors have new vitality. The variable voltage variable frequency speed regulation system of synchronous motor can be divided into other control variable frequency speed regulation and self-controlled frequency conversion speed regulation.For other control frequency conversion speed regulation, similar to the frequency conversion speed regulation of asynchronous motor, it can also be controlled by SVPWM and other control methods according to its mathematical model, and its performance is even better than that of ordinary AC asynchronous motors.Self-controlled variable frequency synchronous motors used to have many names in the development process, such as motors without commutators; when permanent magnets are used and three-phase sine waves are input, they can be called sine wave permanent magnet synchronous motors; and if square waves are input, then It can be called a trapezoidal wave permanent magnet synchronous motor. Yes, this is similar to the brushless DC machine (BLDM) mentioned before. Do you feel that you have turned back after a big circle, but you are now concerned about variable frequency and variable speed. The understanding must be a step deeper, so the DC input is used for the brushless DC motor, but the frequency conversion technology of the synchronous motor is used (the structure is the same as that of the permanent magnet synchronous motor), and the DC brushless motor is used on the Model3.Single-phase AC asynchronous motor - single-phase AC series motor (with brush)Single-phase AC series motor, commonly known as series motor or universal motor (Universal Motor is called abroad, named after AC and DC), the armature winding and the field winding work in series.Single-phase series-wound motors are also called AC-DC dual-purpose series-wound motors, which can work with both AC and DC power sources.The advantages of the single-phase series motor are that it has high speed, large starting torque, small size, light weight, is not easy to stall, and has a wide range of applicable voltages. It can be adjusted by voltage regulation, which is simple and easy to implement.Therefore, it is widely used in electric tools, such as angle grinders, electric drills, etc.The structure of single-phase series-excited motor is very similar to that of DC series-excited motor. The main difference is that the stator core of single-phase series-excited motor must be made of laminated silicon steel sheets, while the magnetic poles of DC can be laminated or laminated. make a whole structure.Most of the speed regulation of single-phase series-excited motors adopts the method of regulating voltage, which is to change the electromotive force.The controllable phase-shift voltage regulation method adopted in the voltage speed regulation method of the single-phase series-excited motor uses the trigger voltage of the thyristor to lag behind the input voltage to realize the phase-shift trigger of the input voltage.There are hardware and software methods in the realization method.It adopts voltage regulation method and SCR speed control technology, which has the characteristics of simple circuit and small component size, and is a simple and effective method for SCR.(a) AC current change curve;(b) When the current is a positive half wave, the direction of rotation of the rotor (c) When the current is a negative half wave, the direction of rotation of the rotorSingle-phase AC asynchronous motor - single-phase AC squirrel cage motor (brushless)When the single-phase current passes through the armature winding, it produces a pulsating magnetic field instead of a rotating magnetic field, so the single-phase asynchronous motor cannot start itself.In order to solve the starting problem, the asynchronous motor powered by single-phase AC is actually often made into two-phase.The main winding is directly powered by a single-phase power supply; the auxiliary winding is spatially different from the main winding by 90° (electrical angle, equal to the mechanical angle divided by the number of pole pairs of the motor).The auxiliary winding is connected to a single-phase AC power supply after being connected in series with a capacitor or resistor, so that the current passing through it has a certain phase difference with the current in the main winding.Make the synthetic magnetic field an elliptical rotating magnetic field, even close to a circular rotating magnetic field.The electric motor thus obtains a starting torque.The motor using the resistance phase separation method is cheap, for example, the auxiliary winding can be wound with thinner wires, but the phase separation effect is poor, and energy is consumed on the resistance.After this kind of motor starts and reaches a certain speed, the centrifugal switch installed on the motor shaft usually cuts off the auxiliary winding automatically to reduce the loss on the resistance and improve the operating efficiency.It is generally used in occasions where the starting torque is not high, such as small lathes, small refrigerators, etc. The disadvantage is that the speed cannot be adjusted.The effect of using capacitor phase separation is better, and it is possible to make the motor's synthetic magnetic field close to the circular rotating magnetic field at a certain working point of the motor, so as to obtain better working characteristics.In order to make the split-phase asynchronous motor obtain better starting performance or better operating characteristics or both, the required capacitance (value) is different, which can be divided into three typesStepper Motors - Open Loop Stepper Motors(Open-loop) stepper motor is an open-loop control motor that converts electrical pulse signals into angular displacements, and is widely used.In the case of non-overload, the speed and stop position of the motor only depend on the frequency and number of pulses of the pulse signal, and are not affected by the load change. When the stepper driver receives a pulse signal, it drives the stepper motor to rotate A fixed angle, called "step angle", its rotation runs step by step at a fixed angle.The angular displacement can be controlled by controlling the number of pulses, so as to achieve the purpose of accurate positioning; at the same time, the speed and acceleration of the motor rotation can be controlled by controlling the pulse frequency, so as to achieve the purpose of speed regulation. (video portal)The stepper motor is a kind of induction motor, and its working principle is to use the electronic circuit, that is, the driver, to convert the direct current into a multi-phase sequence control current for time-sharing power supply.Although a stepper motor is powered by DC current, it cannot be understood as a DC motor. A DC motor is a power motor that converts DC electrical energy into mechanical energy, while a stepper motor is an open-loop control motor that converts electrical pulse signals into angular displacement.Stepper Motor - Stepper Servo ComparisonNote that the stepper motor is used in low-speed occasions - the speed per minute does not exceed 1000r/min, and the best working range is 150~500r/min, (closed-loop stepping can reach 1500).2-phase stepper motors are prone to low-speed resonance at 60~70r/min, resulting in vibration and noise, which need to be avoided by changing the reduction ratio, increasing the number of subdivisions, and adding magnetic dampers.Precautions for subdivision accuracy. When the subdivision level is greater than 4, the accuracy of the step angle cannot be guaranteed, and the accuracy requirement is high. It is best to use a stepper motor with more phases (that is, a smaller step angle) or a closed-loop stepper. ,servo motor.(Open loop) stepper motors are 7 different from servo motors:A control accuracy - servo motor control accuracy can be set according to the encoder, the accuracy is higher;B low frequency characteristics - stepping motors are easy to vibrate at low frequencies, but servo motors will not;C Torque-frequency characteristics——The torque of stepper motors becomes smaller as the speed increases, so its maximum operating speed is generally <1000r/min, and the servo motor can output rated torque within the rated speed (generally 3000r/min). The above is constant power output, the maximum speed can reach 5000 r/min;D Overload capacity - the stepper motor cannot be overloaded, and the maximum torque of the servo motor can be overloaded by 3 times;E running performance - open-loop control for stepping motors, closed-loop control for servo motors;F speed response - stepper motor start time 0.15~0.5s, servo motor 0.05~0.1, the fastest can reach the rated 3000r/min in 0.01s;G efficiency index - the efficiency of the stepper motor is about 60%, and the efficiency of the servo motor is about 80%;In actual use, it will be found that servo motors are expensive and much more expensive, so synchronous motors are more widely used, especially in occasions such as synchronous belt drives and flat belt conveyors that do not require high positioning accuracy. Stepper motors are often used.Stepper Motors - Closed Loop Stepper MotorsClosed-loop stepper motor: In addition to the open-loop stepper motor, there is also a stepper motor with an encoder added to the end of the motor to achieve closed-loop control.The closed-loop control of the stepper motor uses position feedback and (or) speed feedback to determine the phase conversion that is compatible with the rotor position, which can greatly improve the performance of the stepper motor.A servo system without out-of-synchronization phenomena. Advantages of closed-loop stepper motors:1. High-speed response. Compared with the servo motor, the closed-loop stepper has a very strong followability to the positioning command, so the positioning time is very short. In applications with frequent starts and stops, the positioning time can be significantly reduced.2. Generate larger torque than normal servo. It makes up for the out-of-step and low-speed vibration of ordinary stepping systems.3. It can also generate high torque under 100% load condition, no out of step operation, no need to consider torque loss and other issues like ordinary stepping systems.4. Apply closed-loop drive, the efficiency can be increased to 7.8 times, the output power can be increased to 3.3 times, and the speed can be increased to 3.6 times.Can get higher operating speed than open-loop control, more stable and smoother speed.5. The stepper motor will be completely still when it stops, without the micro-vibration phenomenon of ordinary servo.Where low-cost, high-precision positioning is required, it can replace the application of general-purpose servo systems.Stepper Motor - Stepper Closed Loop Servo ComparisonThe closed-loop stepping motor automatically adjusts the winding current according to the load size. The heat and vibration are less than that of the open-loop stepping motor. With encoder feedback, the precision is higher than that of the ordinary stepping motor. The motor response is slower than the open-loop stepping motor and faster than the servo motor. There is a position error in the center, and the error will gradually decrease after a few milliseconds after the command stops.High-speed torque is larger than that of open-loop stepping, and it is commonly used in 0-1500rpm occasions.Summary: The closed-loop stepper motor has the characteristics of low cost, high efficiency, no jitter, no stop micro-vibration, high rigidity, no tuning, high speed, high dynamic response, etc. It is a cost-effective alternative to high-cost servo systems and low-end open-loop stepper systems. highest solutionServo motor - common servo motorServo motor (servo motor) is also called executive motor, which can control the speed and position accuracy very accurately, and can convert the voltage signal into torque and speed to drive the controlled object.Different from the principle structure of the stepper motor, the servo motor puts the control circuit outside the motor, and the motor part inside is a standard DC motor or AC induction motor.The servo motor is positioned by pulses, and the servo motor will rotate by the angle corresponding to one pulse when it receives one pulse.Every time the motor rotates an angle, the encoder will send a corresponding number of feedback pulses, and the feedback pulses and the pulses received by the servo driver form a closed-loop control, so that the servo driver can accurately control the rotation of the motor to achieve precise positioning.Servo motor control: Generally, industrial servo motors are controlled by three loops, namely, current loop, speed loop, and position loop, which can respectively feed back the angular acceleration, angular velocity, and rotational position of the motor.The chip controls the drive current of each phase of the motor through the feedback of the three, so that the speed and position of the motor can be operated accurately and as scheduled. The AC servo has the characteristic of constant torque at the rated speed. The common 200W, 400W low and medium inertia AC servo has a rated speed of 3000rpm, and the maximum speed is 5000rpm, which is high.The torque is proportional to the current, and it can work in torque mode, such as locking screws, crimping terminals and other occasions that require constant torque.The AC servo has very little noise and vibration, and low heat generation.Under the same volume, the motor inertia and rotor inertia are small, and the 400W servo inertia is only equivalent to the rotor inertia of a 57-base 2NM stepping motor.The servo has a short-term overload capability, and the overload multiple of the motor during acceleration and deceleration should be considered when selecting the model.The servo adopts closed-loop control, which has the same position tracking error as closed-loop stepping.The servo needs to be debugged before it can be used.When the raw torque of the stepping and servo motors is not enough, it is often necessary to work with a reducer, and a reduction gear set or a planetary reducer can be used.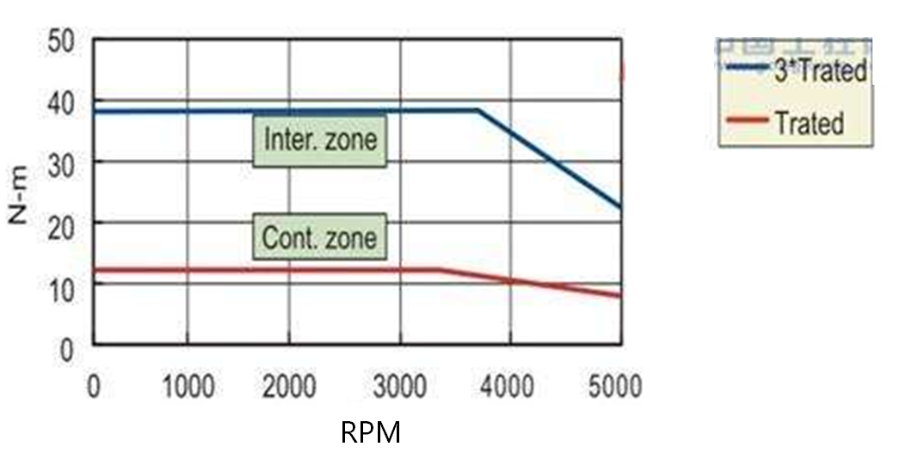 Servo motor - steering gearSteering gear (servo), commonly known by Chinese people, is a type of DC servo motor, first used in small model aircraft, and now used in small robot joints.In terms of structure, the steering gear includes a small DC motor, plus sensors, control chips, and reduction gear sets, which are packed into an integrated casing.The rotation angle can be controlled by an input signal (usually a PWM signal, but also a digital signal).Because it is a simplified version, the original three-loop control of the servo motor is simplified into one loop, that is, only the position loop is detected.A cheap solution is a potentiometer, which is detected by a resistor, and an advanced solution uses a Hall sensor, or a grating encoder.General steering gear is cheap and compact, but its accuracy is very low and its position stabilization ability is poor, which can meet many low-end needs.With the upsurge of consumer-grade small robots in the past two years, small and lightweight servos have suddenly become the most suitable joint components.However, the performance requirements of robot joints are much higher than those of rudders, and as a commercial product, the quality of rudders is much higher than that of DIY players.
Servo motor - steering gearSteering gear (servo), commonly known by Chinese people, is a type of DC servo motor, first used in small model aircraft, and now used in small robot joints.In terms of structure, the steering gear includes a small DC motor, plus sensors, control chips, and reduction gear sets, which are packed into an integrated casing.The rotation angle can be controlled by an input signal (usually a PWM signal, but also a digital signal).Because it is a simplified version, the original three-loop control of the servo motor is simplified into one loop, that is, only the position loop is detected.A cheap solution is a potentiometer, which is detected by a resistor, and an advanced solution uses a Hall sensor, or a grating encoder.General steering gear is cheap and compact, but its accuracy is very low and its position stabilization ability is poor, which can meet many low-end needs.With the upsurge of consumer-grade small robots in the past two years, small and lightweight servos have suddenly become the most suitable joint components.However, the performance requirements of robot joints are much higher than those of rudders, and as a commercial product, the quality of rudders is much higher than that of DIY players.






 Servo motor - steering gear
Servo motor - steering gear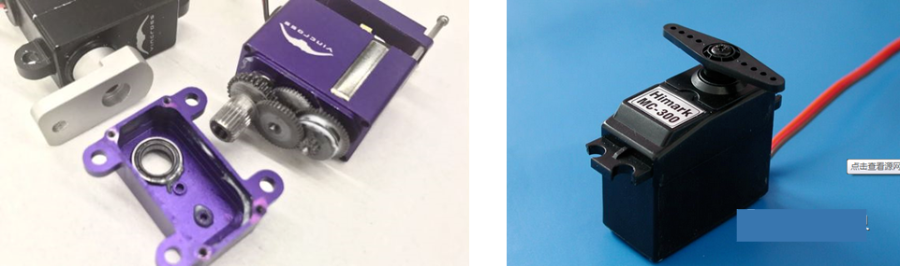



























 XINDA
XINDA