Influence of silicon steel sheet consolidation method on modal characteristics of new energy vehicle
Research on the influence of silicon steel sheet consolidation method on the modal characteristics of new energy vehicle motor
Motor is one of the main noise sources of new energy vehicles, and it has become a hot research topic in recent years. The stator core is the main noise source of the motor noise. The increase of the motor speed makes the operating frequency continuously increase, and high-frequency resonance with the stator is easy to occur. Since the processing technology of the stator core will affect the modal frequency of the stator, it can be optimized by optimizing the stator core. The advanced consolidation process improves the vibration characteristics of the stator to achieve the purpose of reducing vibration and noise of the motor.
The common consolidation methods of stator core laminations include bonding and welding, both of which may affect the natural frequency and mode shape of the stator. Bonding is a commonly used consolidation process for motor stators. The stator silicon steel sheets are grouped, and the silicon steel sheets in the group are bonded with an adhesive and assembled by a hydraulic press. The laminated sheets are baked and cooled under pressure, and then formed. The stator The iron core can be regarded as a composite material composed of silicon steel sheets and insulating adhesives; welding is also a common consolidation process for stators. First, the silicon steel sheets are stacked and formed, fixed with a hydraulic press, and then continuous laser welding is used along the weld seam of the iron core. , Weld the silicon steel sheets together from top to bottom.
The research on bonded iron cores at home and abroad mainly focuses on the modeling and analysis of the laminated structure, and mainly explores the influence of welding process on the static mechanical properties of the iron core, but the influence of the iron core consolidation method on its dynamic characteristics is still unknown .
Researchers such as Song Jinyuan of Shanghai Jiaotong University believe that direct numerical analysis of the stator will consume a large amount of computing resources and time costs, and propose a dynamic modeling method for the two joining processes of bonding and welding, and design the modal experiment of the stator core: The lamination theory is used for the dynamic modeling of the bonded stator, the simplified modeling for the welded stator is based on the semi-finite element method, and then the accuracy of the model is verified by the modal experiment of the stator, and finally a vibration reduction method is proposed for the welded stator Structural optimization design for noise reduction. This project is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
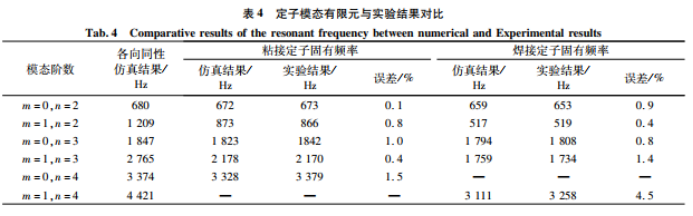
The researchers studied the stator cores with two different consolidation processes, and proposed two modeling methods for the stator cores. Di corrected the finite element model through experiments, and the final finite element results were consistent with the experimental results. The following conclusions can be drawn:
(1) The material properties of the bonded stator can be calculated according to the classical lamination theory, showing obvious orthotropy.
(2) The welded stator also exhibits orthotropy. The semi-finite element method proposed in this paper allows accurate dynamic modeling of welded stators.
(3) The consolidation mode of the stator mainly affects the modes with different numbers of pitch diameters of the stator core, has little effect on the modes with different numbers of pitch circles, and has a great influence on the torsional modes of the welded stator. The natural frequency of the welded stator is smaller than that of the bonded stator.
(4) Taking the motor composed of the experimental stator as an example, based on the method proposed in this paper, it is deduced that the optimal number of welds for the stator is 8 or 12.





























 XINDA
XINDA