A full explanation: motor rotation principle, structure, type, troubleshooting
Motors are ubiquitous in the field of equipment. Motor type, soft start method, selection steps, damage causes and treatment methods, what is the difference between good and bad motors... Let's take a look together in this issue.

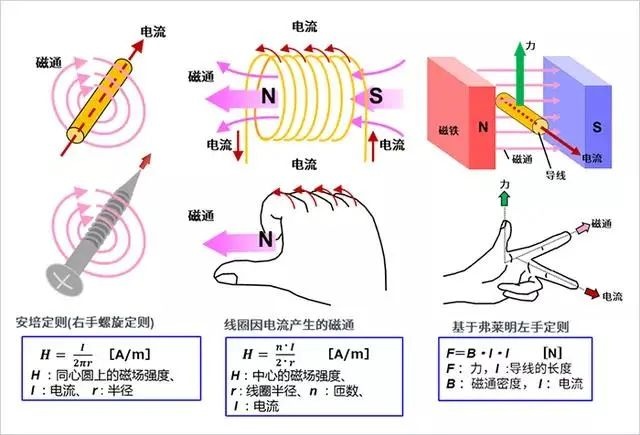
1. Electric current, magnetic field and force
First, for the convenience of the subsequent explanation of the principle of electric machines, let's review the basic laws/laws concerning electric current, magnetic field and force. Although there is a sense of nostalgia, it is easy to forget this knowledge if you do not use magnetic components regularly.
2. Detailed explanation of rotation principle
The following describes the rotation principle of the motor. We combine pictures and formulas to illustrate.
When the leadframe is rectangular, take into account the forces acting on the current flow.
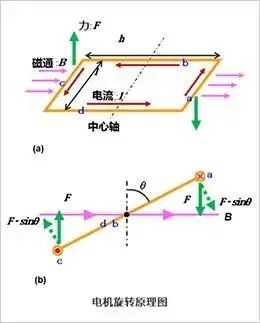
The force F acting on sides a and c is:

Generates torque about the central axis.
For example, when considering the state where the rotation angle is only θ, the force acting at right angles to b and d is sinθ, so the torque Ta of part a is expressed by the following formula:
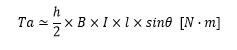
Considering part c in the same way, the torque is doubled and results in a torque calculated by:

Since the area of the rectangle is S=hl, substituting it into the above formula yields the following result:
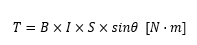
This formula works not only for rectangles, but also for other common shapes like circles. Electric motors take advantage of this principle.
Key Takeaways:
The principle of rotation of a motor follows laws (laws) related to current, magnetic field and force.


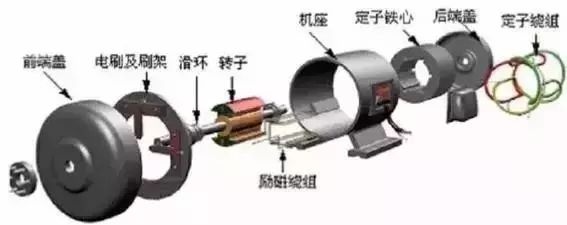
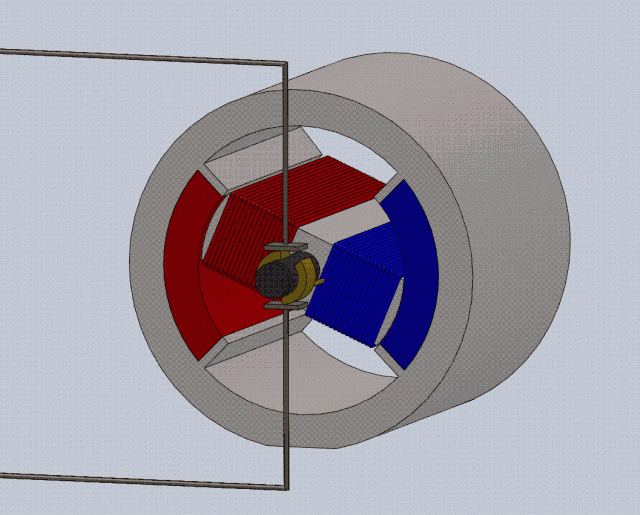




(1) Structure:
Rotor: squirrel cage
Stator: 3 windings
(2) Principle:
Three-phase asynchronous motor (Triple-phase asynchronous
motor) is a kind of induction motor. At the same time, 380V three-phase AC current (phase difference 120 degrees) is connected to form a rotating magnetic field, and the squirrel cage generates an induced current, and then moves. The movement is realized by induction, the stator rotates the magnetic field to cut the squirrel cage, so that the squirrel cage generates an induced current, and the induced current is forced to make the rotor rotate. There must be a speed difference between the rotor speed and the stator rotating magnetic field speed to form a magnetic field cutting the squirrel cage and generate an induced current.
(3) start:
Star-delta start, step-down start.
(4) Commutation:
Swap the wiring of any two connectors in the three phases of the stator.
(5) Speed regulation: Speed regulation is difficult.
(6) Features:
Since the rotor and the stator rotating magnetic field of the three-phase asynchronous motor rotate in the same direction and at different speeds, there is a slip, so it is called a three-phase asynchronous motor. The rotor speed of the three-phase asynchronous motor is lower than that of the rotating magnetic field. The relative motion between the rotor winding and the magnetic field generates electromotive force and current, and interacts with the magnetic field to generate electromagnetic torque to realize energy conversion.
Compared with single-phase asynchronous motors, three-phase asynchronous motors have better running performance and can save various materials. According to different rotor structures, three-phase asynchronous motors can be divided into cage type and wound type. The asynchronous motor with cage rotor has simple structure, reliable operation, light weight and low price, and has been widely used. Its main disadvantage is that it is difficult to adjust the speed.
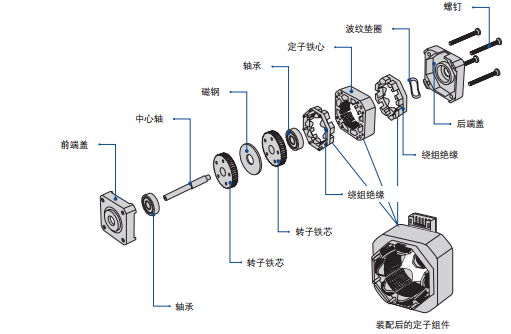
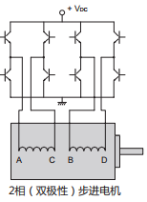

-
DC -
Asynchronous motor -
synchronous motor




























 XINDA
XINDA