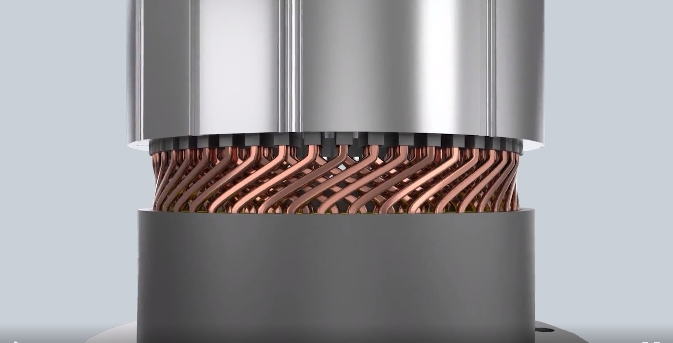
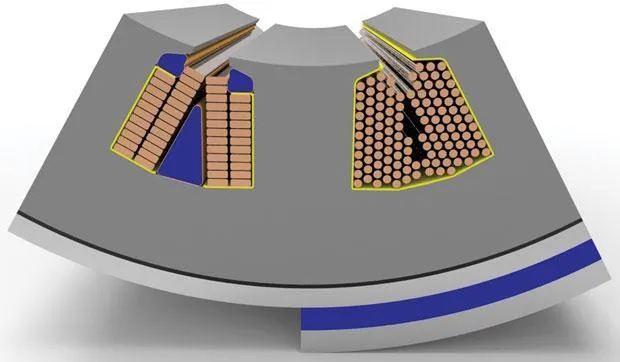
What is the appropriate slot fill rate for motor windings? Is the higher the better?
-
Magnetic circuit design: The magnetic circuit design of the motor is an important factor affecting the stator slot fill rate. By using a suitable magnetic circuit structure and winding arrangement, the number of stator slots can be reduced without reducing performance, thereby increasing the stator slot fill rate.
-
Heat dissipation design: In the case of high stator slot fill rate, heat dissipation is an important issue. Therefore, the design of the radiator and ventilation system needs to be considered in the design to ensure the heat dissipation capacity when the motor is running.
-
Structural design: The structural design of the motor is closely related to the stator slot fill rate. Reasonable design of the geometric shape and size of the stator slot can maximize the use of the stator slot space and improve the stator slot fill rate while meeting performance requirements.
-
Insulation design: High stator slot fill rate places higher requirements on insulation, so it is necessary to consider the selection of insulation materials and the design of winding insulation to ensure that the motor does not fail during operation.



























 XINDA
XINDA