![]()
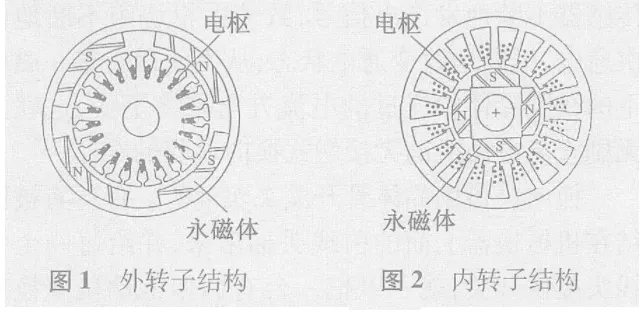
Permanent magnet synchronous motors can be divided into outer rotor structures and inner rotor structures according to the position of the rotor in the motor . The difference is whether it rotates inside or outside. If it rotates inside, it is an inner rotor structure, and if it rotates outside, it is an outer rotor structure.
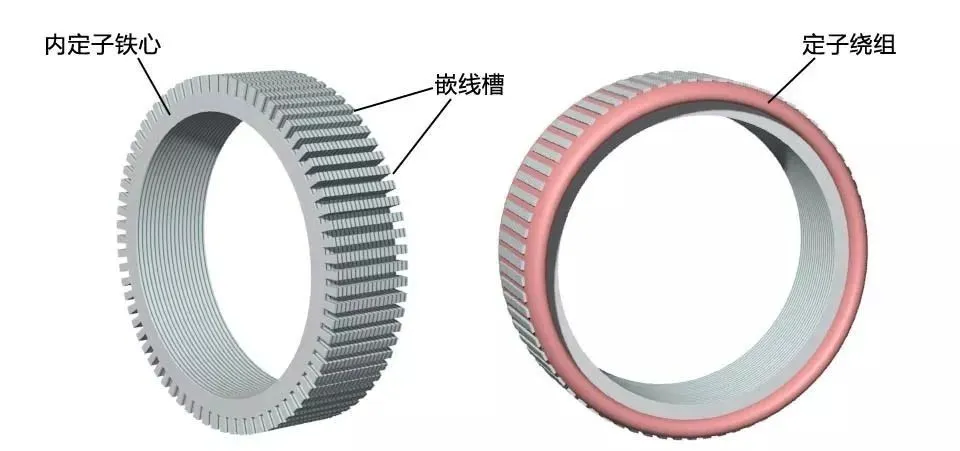
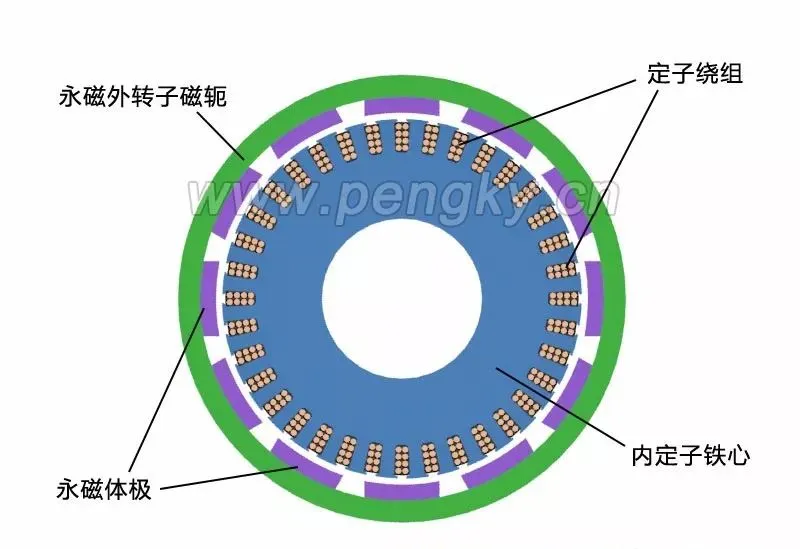
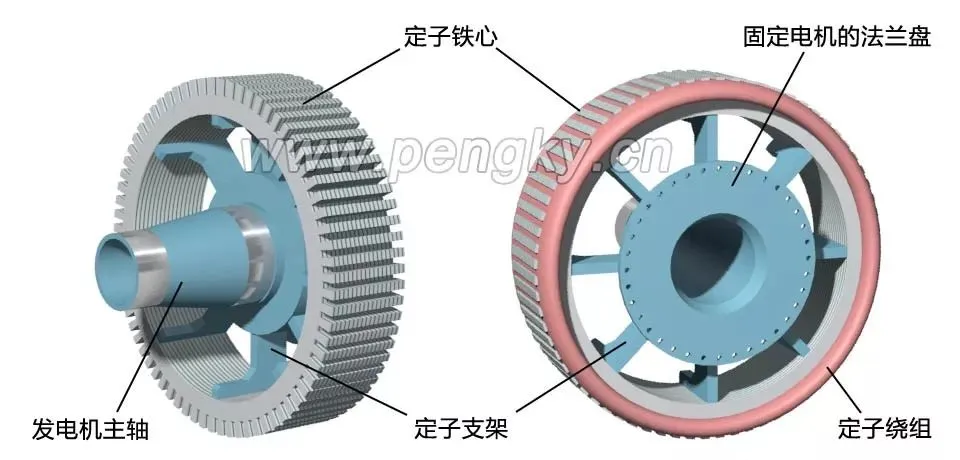
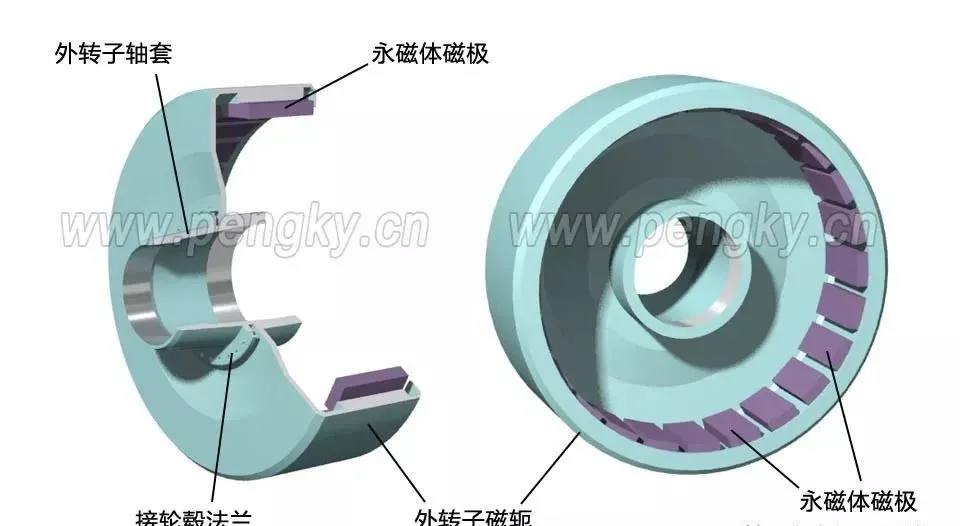
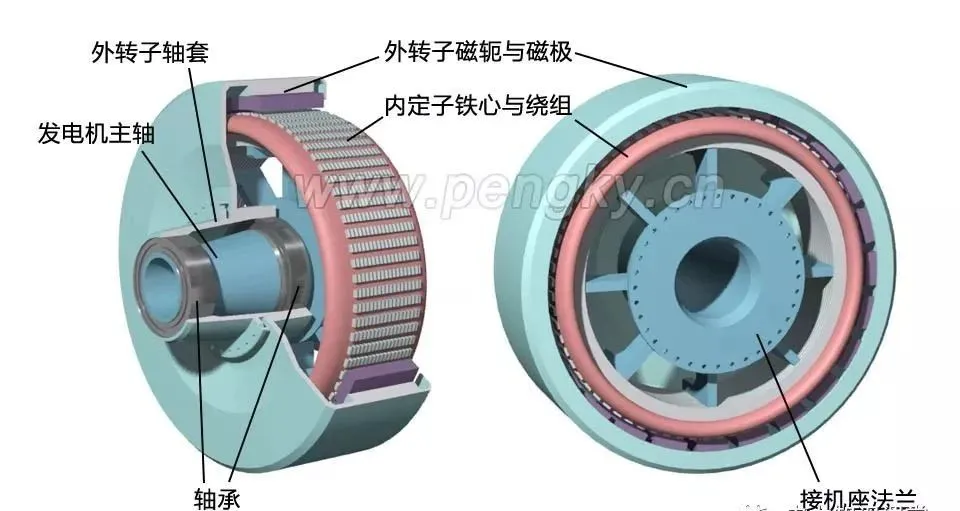
Usually the rotating part is the part with embedded magnetic steel, i.e. the rotor; the non-rotating part is the coil part, i.e. the stator. Let's talk about the difference between the inner rotor and the outer rotor of a permanent magnet motor.In practical applications, there are the following differences between inner rotors and outer rotors:1. Difference in rotational position. The inner rotor, that is, the transmission part of the motor is inside, the outer shell is static, and the inside rotates; the outer rotor is static inside, and the outer shell rotates. Generally speaking, the embedded magnetic steel (permanent magnet) part will rotate, while the coil part will not rotate. According to the permanent magnet embedding process and position, the outer rotor and the inner rotor can also be distinguished.2. Size of permanent magnets. The outer rotor permanent magnets are small in size, small in axial dimension, and have good system operation stability. The inner rotor permanent magnets are large in size, correspondingly larger in axial dimension, high in center of gravity, and poor in operation stability.3. Speed. Taking the same brushless DC motor as an example, the speed of the inner rotor motor is significantly higher than that of the outer rotor motor .4. Application. The inner rotor is often used in power machinery such as motors, generators, gas turbines and compressors, while the outer rotor is usually installed in the impeller to perform heat dissipation and cooling.The characteristic of the outer rotor motor is that the stator is fixed in the middle position near the shaft and does not move, and the rotor rotates on the periphery of the stator. It is also a radial air gap flux structure. Compared with the inner rotor structure, the rotor and stator have switched positions. Figure 1 is a plan view of the outer rotor generator. The stator inside the motor is called the inner stator, and the rotor on the outer periphery of the motor is called the outer rotor.Figure 1—Outer rotor generator plan viewDirect drive outer rotor permanent magnet wind turbineThe following introduces the composition and structure of the direct-drive outer rotor permanent magnet wind turbine generator set. Its structure is introduced through a permanent magnet outer rotor generator model. The left picture in Figure 3 is a diagram of the inner stator core. The stator core is stacked by silicon steel sheets with good magnetic conductivity. There are many slots on the outer periphery of the stator core. The generator winding is embedded in the slots, and the winding is distributed according to the three-phase law.Generally, the outer rotor of a large direct-drive wind turbine has 30 to 40 pairs of poles, and the number of stator slots is about 180 to 240. In order to clearly show the structure of the inner stator core, the number of coil slots in this model is much less than that of an actual direct-drive generator.Figure 2 - Stator core and windings in a direct drive generatorThe stator core is installed on the stator bracket. One end of the stator bracket has a flange installed on the nacelle frame, and the other end is the outer rotor shaft, which is also the main shaft of the wind turbine. The main shaft has to bear the weight and wind force of the entire wind wheel and outer rotor. The main shaft and flange must have high strength.Figure 3 - Direct drive generator internal stator structureFigure 4 is a cross-sectional view of the outer rotor structure, showing its structure in two directions. The outer rotor is like a barrel sleeved outside the stator, made of iron material with good magnetic conductivity, and the inner circumference of the "barrel" is fixed with magnetic poles made of permanent magnets . The "barrel" is the rotor's yoke. One of the advantages of this structure is that the magnetic poles are easier to fix and will not fall off due to centrifugal force. The outer rotor yoke is fixed on the rotor sleeve.Figure 4 - Direct drive generator outer rotor structureThe outer rotor is installed on the main shaft of the generator to form an outer rotor generator. The following figure shows its structure from two directions. The outer rotor sleeve not only fixes the outer rotor, but also installs the entire wind wheel, which bears a large load, so it is installed on the main shaft of the generator through two large bearings.The advantages and disadvantages of inner rotor and outer rotor are:The advantages of the inner rotor include light blades, easy production and assembly of the motor, and low cost, but there are problems such as rapid motor heating, high power consumption, unstable voltage that can easily damage the motor, and short life.The advantage of the outer rotor is that it can be made into a fully enclosed structure, which can run quickly after starting, has low power consumption, high speed, high efficiency and long service life. However, it has poor sealing, large rotor inertia, high noise and high requirements for dynamic balance.




























 XINDA
XINDA