The characteristics of stepper motors, brushed motors, and brushless motors are summarized
Date:2023-11-16 Author:Shandong Xinda Motor Co., Ltd.
The characteristics of stepper motors, brushed motors, and brushless motors are summarized in the table below.
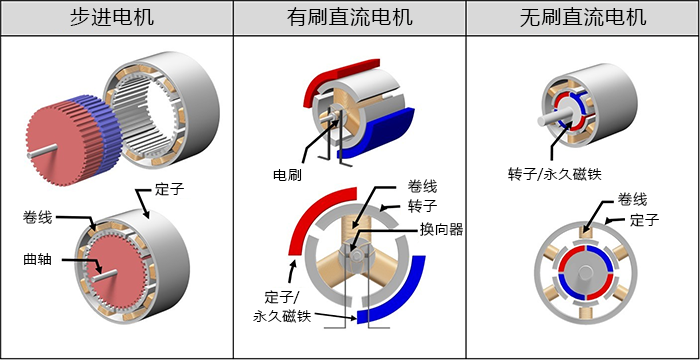
| stepper motor | brushed motor | Brushless Motor | |
|---|---|---|---|
| rotation method | Through the drive circuit, the armature winding is excited in the order determined by the phases (there are two phases, three phases, and five phases). | The armature current is switched by a sliding contact rectifying mechanism of brushes and commutator. | Brushless by replacing the functions of brushes and commutators with magnetic pole position sensors and semiconductor switches |
| Drive circuit | need | unnecessary | need |
| Torque | The torque is relatively large. (especially torque at low speed) | The starting torque is large, and the torque is proportional to the armature current (the torque at medium to high speed is relatively large) | |
| spinning speed | Proportional to the input pulse frequency. There is a out-of-step area in the low speed range | Proportional to the armature applied voltage. Speed decreases as load torque increases | |
| high speed rotation | Difficulty spinning at high speed (need to slow down) | Due to the limitations of the brush and commutator rectification mechanism, it can reach up to several thousand rpm. | It can reach up to several thousand to tens of thousands of rpm. |
| Rotation life | Determined by bearing life. tens of thousands of hours | Limited by brush and commutator wear, several hundred to several thousand hours | Tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of hours are determined by the bearing life. |
| Forward and reverse methods | Need to change the sequence of excitation phases of the drive circuit | Reverse the polarity of the pin voltage to reverse the | Need to change the sequence of excitation phases of the drive circuit |
| Controlling | Open-loop control is possible in which the rotation speed and position (rotation amount) are determined by command pulses (but there is a problem of out-of-step) | Constant speed rotation requires speed control (feedback control using speed sensor) Torque control is easy since torque is proportional to current | |
| Ease of acquisition | Easy: There are many varieties | Easy: Many manufacturers and varieties, many options. | Difficulties: Mainly specialized motors for specific applications |
| price | If the drive circuit is included, the price is more expensive than the brushless motor | Relatively cheap, coreless motors are a bit pricey due to their magnet upgrades | If the driver circuit is included, the price is more expensive |
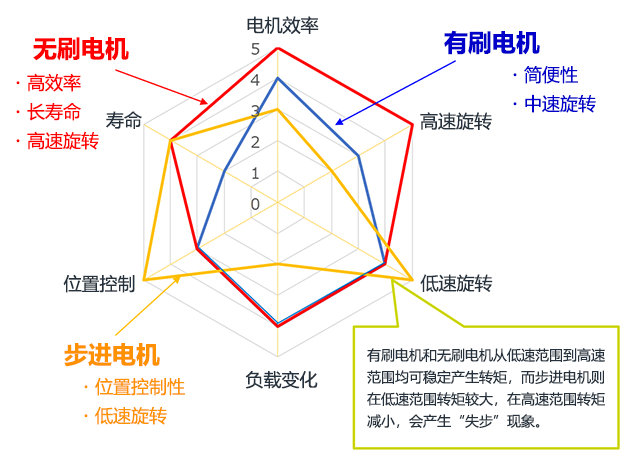
Performance comparison of small motors
A radar chart lists performance comparisons of various small motors.
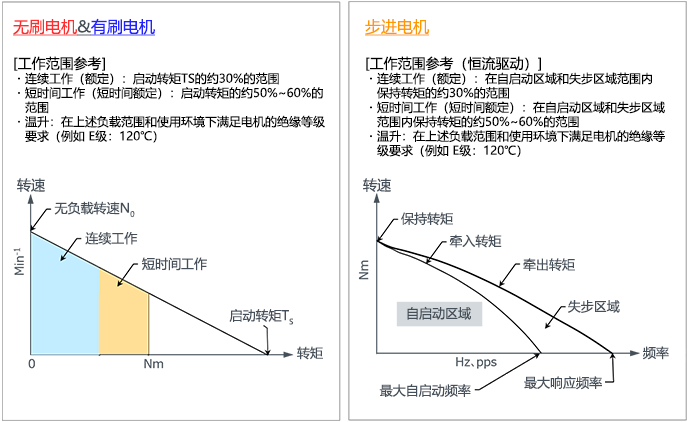
The following summarizes the speed-torque characteristics of each small motor. It can be considered that brushless motors and brushed motors are basically the same.
Key takeaways
-
The characteristics, performance, and characteristic comparison results of small motors can be used as a reference when selecting motors. -
Motors in the same category include multiple specifications, so the characteristics, performance, and characteristic comparison results of small motors are only for reference. -
In the end, you still need to confirm the detailed information through the technical specifications of each motor.
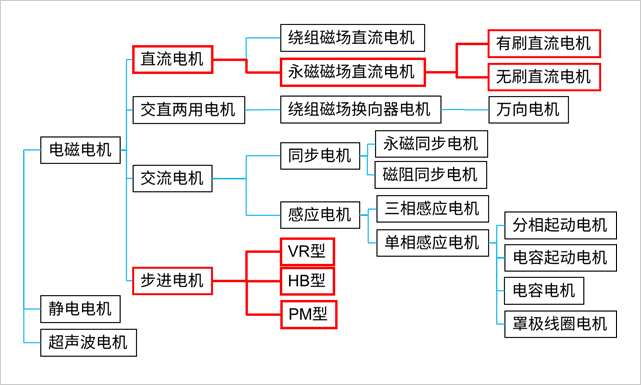
Attachment: Types and classifications of motors



























 XINDA
XINDA