Can the motor core also be 3D printed? New Developments in Research on Magnetic Cores for Motors
Date:2023-07-12 Author:Shandong Xinda Motor Co., Ltd.
The magnetic core is a sheet of magnetic material with high magnetic permeability. They are commonly used for field guidance in a variety of electrical systems and machines, including electromagnets, transformers, motors, generators, inductors and other magnetic components.
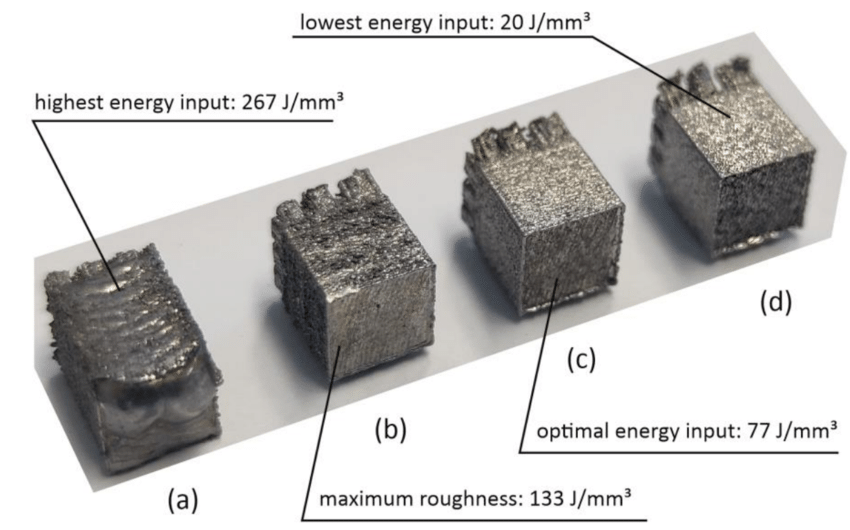
So far, the 3D printing of magnetic cores has been a challenge due to the difficulty of maintaining the efficiency of the magnetic core. But a research team has now proposed a comprehensive laser-based additive manufacturing workflow that they say can produce products with superior magnetic properties to soft magnetic composites.
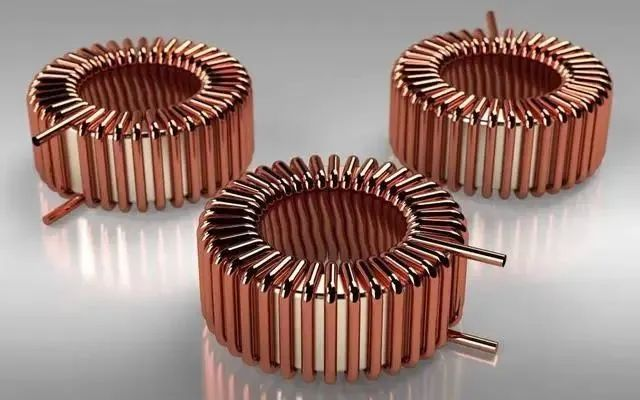
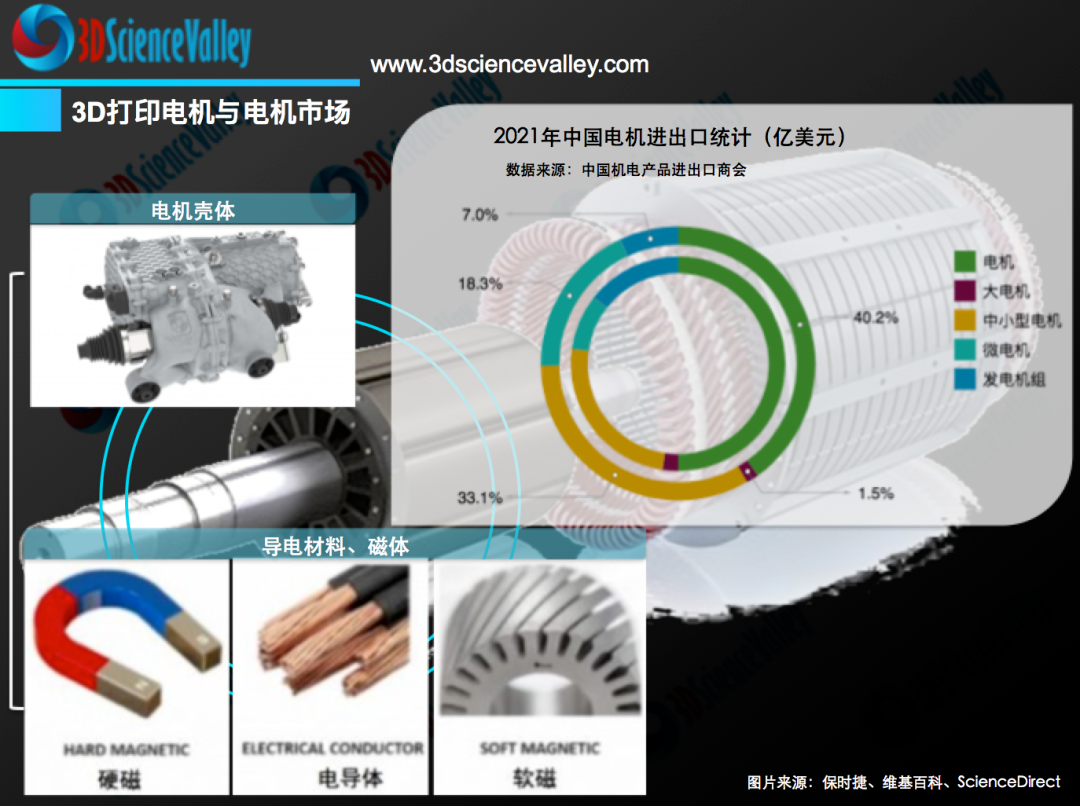
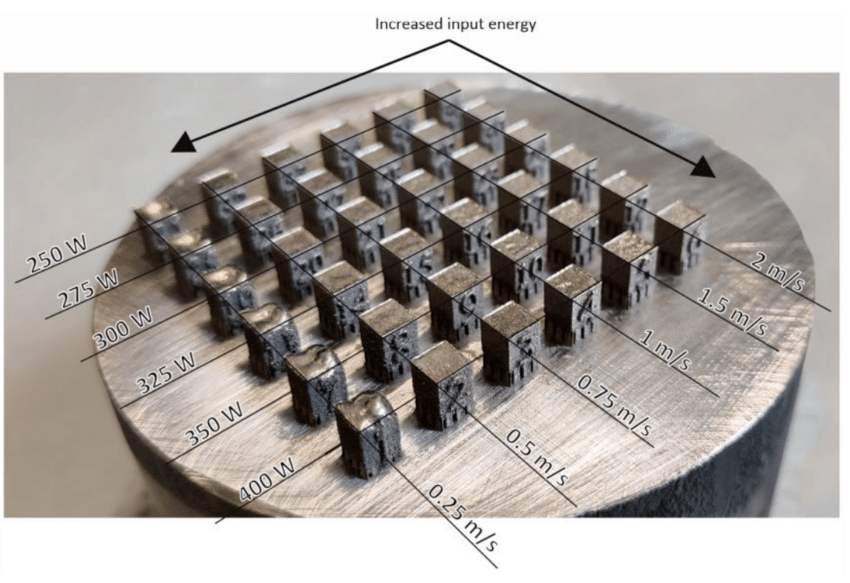
Optimized 3D printing workflow



























 XINDA
XINDA