Is there any difference between motor and electric motor?
what is a motor
Motor (English: Electric machinery, commonly known as "motor") refers to an electromagnetic device that realizes the conversion or transmission of electric energy according to the law of electromagnetic induction.
The motor is represented by the letter M (the old standard is D) in the circuit. Its main function is to generate driving torque as a power source for electrical appliances or various machines. The generator is represented by the letter G in the circuit. Its main function The function is to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy.
1. Motor division and classification
1. According to the type of working power supply: it can be divided into DC motor and AC motor.
2. It can be divided according to the structure and working principle: it can be divided into DC motor, asynchronous motor and synchronous motor.
3. According to the starting and running mode, it can be divided into: capacitor starting single-phase asynchronous motor, capacitor running single-phase asynchronous motor, capacitor starting running single-phase asynchronous motor and split-phase single-phase asynchronous motor.
4. According to the application, it can be divided into: drive motor and control motor.
5. According to the structure of the rotor, it can be divided into: cage induction motor (the old standard is called squirrel cage asynchronous motor) and wound rotor induction motor (the old standard is called wound asynchronous motor).
6. According to the operating speed, it can be divided into high-speed motors, low-speed motors, constant-speed motors, and speed-adjustable motors. Low-speed motors are further divided into gear reduction motors, electromagnetic reduction motors, torque motors and claw pole synchronous motors.
2. What is a motor
A motor is a device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. It uses energized coils (that is, stator windings) to generate a rotating magnetic field and acts on the rotor (such as a squirrel-cage closed aluminum frame) to form a magneto-electric power rotation torque. Motors are divided into DC motors and AC motors according to the power used. Most of the motors in the power system are AC motors, which can be synchronous motors or asynchronous motors (the motor stator magnetic field speed and rotor rotation speed do not maintain synchronous speed). The motor is mainly composed of a stator and a rotor. The direction of the current-carrying wire in the magnetic field is related to the direction of the current and the direction of the magnetic field line (magnetic field direction). The working principle of the motor is that the magnetic field acts on the force of the current to make the motor rotate.
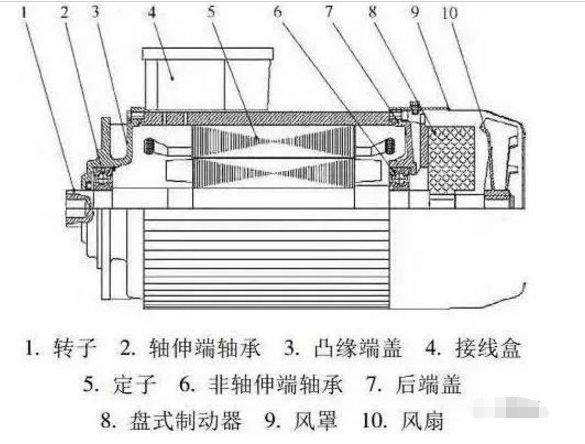
Three, the basic structure of the motor
1. The structure of a three-phase asynchronous motor consists of a stator, a rotor and other accessories.
2. The DC motor adopts an octagonal fully laminated structure and a series excitation winding, which is suitable for automatic control technology that requires forward and reverse rotation. According to user needs can also be made with series winding. Motors with a center height of 100-280mm have no compensation windings, but motors with a center height of 250mm and 280mm can be made with compensation windings according to specific conditions and needs, and motors with a center height of 315-450mm have compensation windings. The external installation dimensions and technical requirements of the motor with a center height of 500-710mm conform to the IEC international standard, and the mechanical dimension tolerance of the motor conforms to the ISO international standard.



























 XINDA
XINDA