Explanation of motor knowledge, from motor classification to selection
Date:2022-09-21 Author:Shandong Xinda Motor Co., Ltd.
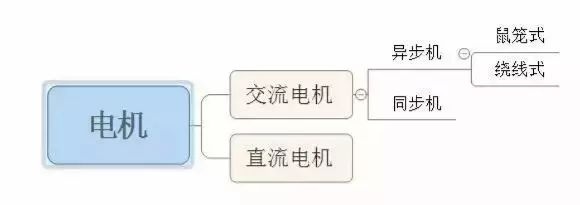
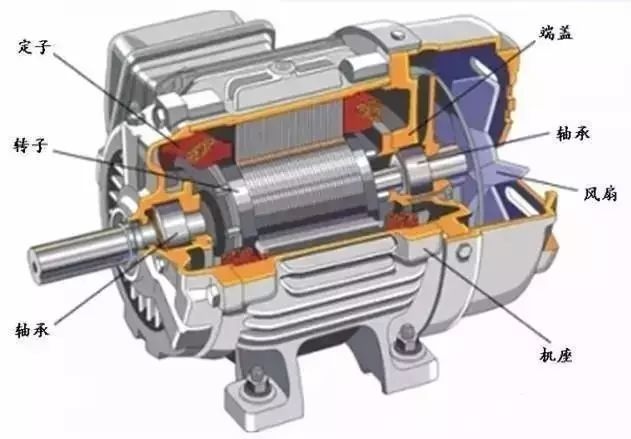
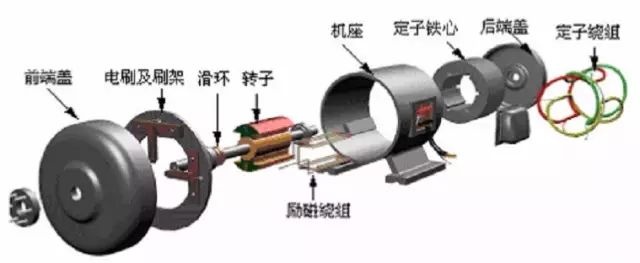



Production machinery that requires a large starting torque and soft mechanical characteristics, uses series or compound excitation DC motors, such as trams, electric locomotives, heavy cranes, etc.



























 XINDA
XINDA