What are the energy losses of the permanent magnet motor?
What are the energy losses of the permanent magnet motor, and how to use these losses to reconstruct the motor model?
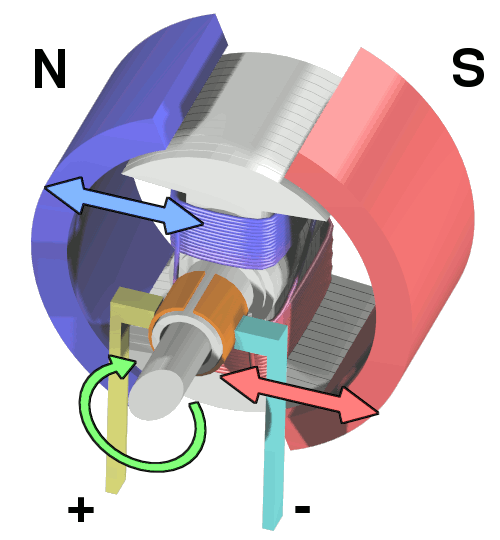
The motor is a conversion mechanism between electric energy and kinetic energy. The actual energy conversion of the permanent magnet motor is as follows: the input electric energy flows through the conductive coil of the motor, and is converted into magnetic energy by the electromagnetic effect. The characteristics of the same poles repelling the opposite poles and attracting each other form relative motion on the rotor of the motor to generate mechanical kinetic energy output. It can be seen that the permanent magnet motor system has three energy forms: electrical, magnetic and mechanical. In order to incorporate the actual loss of the permanent magnet motor into the system and redefine the mathematical model of the permanent magnet motor, it is necessary to analyze the various losses of the permanent magnet motor first.
From the second law of thermodynamics, it can be known that there will be losses in the process of energy transmission and conversion, and energy cannot be transmitted 100%. Permanent magnet motors can be divided into three categories: electrical energy loss, magnetic energy loss and mechanical loss. After dividing it into detail, it can be sorted into the following losses: voltage drop loss, copper loss, hysteresis loss, eddy current loss, friction loss, viscous loss and wind loss.
Voltage drop loss
The voltage drop loss is a kind of electrical loss, which is caused by the motor power connection line and the inverter. The motor needs to transmit power to the motor coil through the power connection line and the inverter. The motor coil has a resistance value, and the power connection line and The commutator also has a resistance value; it can be seen from the circuit that the series connection of the two resistors will produce a voltage dividing effect, which will cause the motor coil to be affected by the voltage drop, that is, the actual voltage across the motor coil is lower than the input voltage value.
Copper loss
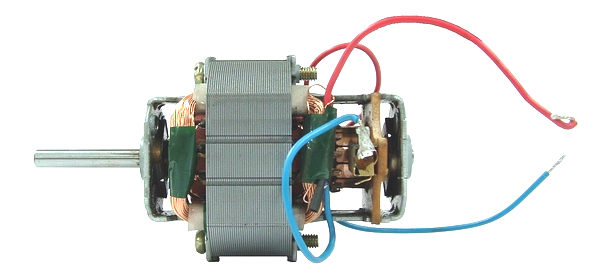
Copper loss is also a type of electrical loss, which refers to the electrical energy transmission loss caused by the material impedance when the current passes through the conductive material. Show. The motor coil generally uses copper with lower impedance value as the conductive material, so the conduction loss of the motor is directly referred to as the copper loss.
iron loss
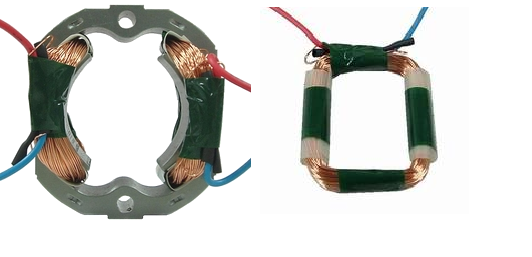
Iron is the most well-known magnetic conductive material. It is often called the magnetic conductive material of the motor as the iron core. In practical applications, most of the silicon steel sheets with high saturation magnetic flux density and low loss are used as the magnetic conductive material for the motor. The silicon steel sheet is as follows shown. The losses generated by the magnetically conductive material are collectively referred to as iron loss, including hysteresis loss and eddy current loss, both of which are losses caused by the transmission and conversion of magnetic energy in the magnetically conductive material.
Hysteresis loss
Any energy will be lost in the process of transmission and transformation, and magnetic energy is no exception. Hysteresis loss refers to the energy loss required for the atomic structure of magnetically permeable materials to be rearranged into the magnetic direction when an external magnetic field changes.
Eddy current loss
Eddy current loss is also the loss caused by the magnetic conductive material, which belongs to a kind of magnetic energy loss; it is caused by the instantaneous magnetic field change when the motor rotates and commutates, and the induced current flows in the magnetic conductive material, resulting in loss.
friction loss
Friction loss is a kind of mechanical loss. When an object is moving, a force in the opposite direction will be generated on the contact surface with other things, and it will resist the force in the moving direction, which is friction loss. Friction loss can be subdivided into static friction loss and dynamic friction loss; static friction loss describes that when an object starts to move, it needs to exert a large force to overcome the static friction force of the contact surface before it can start to move; when the object continues to move , there is still a constant friction force on the contact surface, that is, the kinetic friction force.
Theoretically, the friction force will be affected by the speed parameters, but the affected speed range is very small, and there is a significant difference only at the moment of starting to move. In loss analysis, friction can be regarded as a fixed loss independent of speed.
viscous loss
Viscous loss is also a kind of mechanical loss. When the object is moving, there will be a viscous force on the contact surface with the fluid. The motor is affected by the air fluid on the rotor and the viscous resistance caused by the bearing lubricating oil. Its characteristics are: The magnitude of the viscous force is proportional to the speed.
wind damage
Wind loss is the positive fluid resistance in the moving direction of the object. It is the air flow caused by the rotation in the motor, and the air resistance is derived from the flow field pressure difference due to the limitation of the structure space, so it is called wind. loss, which has a quadratic curve relationship with the speed.
in conclusion
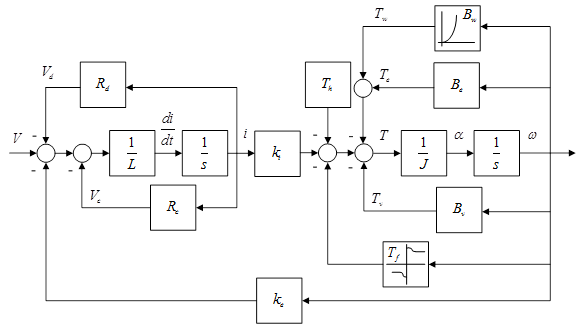
The characteristic parameters of the permanent magnet motor are analyzed in the form of energy, and the actual loss of the motor is imported, and the system model of the permanent magnet motor is reconstructed as follows.




























 XINDA
XINDA