How to measure the shaft voltage of a motor?
The shaft voltage is the potential difference between the two ends of the shaft, the local part of the shaft, and the shaft to the ground during the operation of the motor. When the shaft voltage is high, it may cause the bearing lubricating oil film to be broken down, generate a large shaft current, and cause varying degrees of electrical corrosion to the bearing.
Shaft voltage and shaft current have a great impact on the bearing system of motor products. In order to accurately measure the magnitude of shaft voltage, the 2023 version of GB/T 1032 standard specifically regulates the measurement of motor shaft voltage. The relevant content is now sorted out and shared with everyone.
The picture in this article is a simplified diagram of shaft voltage measurement. Before the test, the insulation resistance between the bearing seat and the metal gasket, and between the metal gasket and the metal base should be checked to ensure that the motor is well insulated. Install an insulating ring between the motor bearing and the housing (insert a dry insulating sheet between the bearing and the shaft) or use an insulating bearing to ensure that the motor bearing is well insulated.
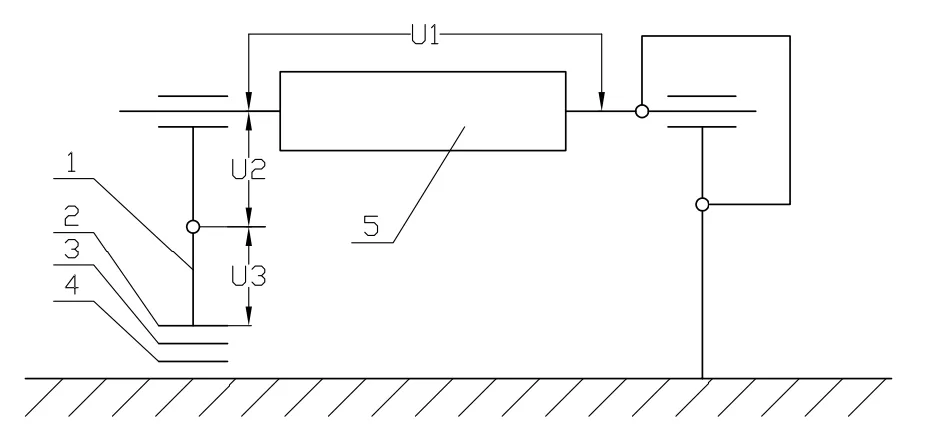
In the figure, number 1 is the bearing seat, numbers 2 and 4 are insulating gaskets, number 3 is the metal gasket, and number 5 is the motor rotor.
The first measurement is carried out under no-load condition. The motor under test should be operated under rated voltage and rated frequency . The shaft voltage U1 is measured with a high internal resistance millivoltmeter . Then, one end of the shaft is short-circuited with the ground with wire A, and the shaft voltage U3 of the other bearing seat to the ground is measured . After the measurement, wire A is removed. The contact between the surface of the measuring point and the lead of the millivoltmeter should be good during the test. From a theoretical analysis, the magnetic field of the motor is the strongest under no-load condition, so the corresponding shaft voltage should also be the largest. The shaft voltage measured at this time should be the maximum value of the entire operation process of the motor.
The second measurement is carried out under the rated operating state of the motor. The motor under test runs at rated current, rated frequency and rated load , and the bearing voltage U2 is measured . The magnitude of this voltage directly affects the safety of the bearing system; according to some empirical data, as long as the voltage does not exceed 350mV, the motor bearing system is relatively safe, otherwise necessary protective measures should be taken. The motor uses insulating bearing sleeves, insulating bearings, or insulates the bearing position of the rotating shaft, which are specific manifestations of circuit-breaking measures. Even if there is shaft voltage, it cannot form a loop, so it will not cause adverse effects on the bearing system.



























 XINDA
XINDA