![]()
When the voltage drops, the motor, as the core component of electric drive, will face a series of significant changes. The following is a detailed discussion of these changes to help better understand how the voltage reduction affects the performance of the motor and its operating status.
1. Current Change
Principle description: According to Ohm's law, the relationship between current (I), voltage (U) and resistance (R) is I = U / R. In a motor, the resistance (R), mainly including the stator resistance and the rotor resistance, is usually fixed, so a decrease in voltage (U) will directly lead to an increase in current (I). The current change characteristics of different types of motors may vary.
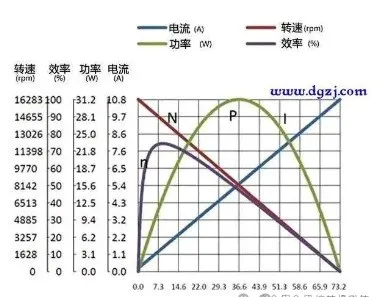
DC Motor: Whether it is a brushless DC motor (BLDC) or a brushed DC motor, when the voltage is reduced and the load remains the same, the current will increase significantly. This is necessary to maintain the original torque output.For asynchronous motors, although the motor adapts to the load by automatically reducing the speed when the voltage decreases, the current may still rise when the load is heavy or changes rapidly.When the voltage of a synchronous motor decreases, if the load remains unchanged, the current will theoretically not change much; but if the load increases, the current will also increase.2. Changes in torque and speedTorque change: A voltage reduction usually results in a reduction in motor torque. Torque is proportional to the product of current and magnetic flux. When the voltage is reduced, although the current increases, the magnetic flux may decrease due to insufficient voltage, resulting in a decrease in overall torque. However, in some cases, such as in DC motors, if the current is increased enough, it can offset the effect of the reduction in magnetic flux to a certain extent, so that the torque remains relatively stable.Speed change: For AC motors, especially asynchronous motors and synchronous motors, a voltage reduction will directly lead to a speed reduction. This is because the motor speed is related to the power supply frequency and the number of motor poles, and the voltage reduction will affect the electromagnetic field strength of the motor, thereby reducing the speed. For DC motors, the speed is proportional to the voltage, so when the voltage is reduced, the speed will also decrease accordingly.3. Efficiency and heat generationReduced efficiency: When the voltage is reduced, the motor efficiency will decrease. When the motor runs at a lower voltage, more current is required to maintain the same output power, which increases the copper and iron losses of the motor, thus reducing the overall efficiency.Increased heat generation: Due to increased current and decreased efficiency, the motor will generate more heat during operation. This will not only accelerate the aging and wear of the motor, but may also trigger the overheating protection device, causing the motor to shut down.Long-term operation under unstable or low voltage conditions will seriously shorten the service life of the motor. A series of problems caused by voltage reduction - increased current, torque fluctuations, reduced speed and reduced efficiency - will damage the internal structure and electrical performance of the motor. In addition, the increased heat generation will accelerate the aging process of the motor's insulation materials.To mitigate the impact of voltage reduction on the motor, the following measures can be taken:Optimize the power supply system: ensure the voltage stability of the power supply grid to avoid voltage fluctuations causing shocks to the motor.Choose a suitable motor: During the design and selection stage, fully consider the factor of voltage fluctuation and choose a motor with a wider voltage adaptability range.Install a voltage stabilizer: Install a voltage stabilizer or voltage regulator at the motor input to maintain voltage stability.Strengthen maintenance: Regularly inspect and maintain the motor to promptly identify and address potential problems to extend the motor's service life.In short, voltage reduction has many effects on motors, including current changes, torque and speed changes, efficiency and heating issues, and impact on motor life, etc. Therefore, in practical applications, it is crucial to take effective measures to mitigate these effects and ensure the safe and stable operation of the motor.




























 XINDA
XINDA