High-efficiency energy-saving motors can actually save so much electricity!
High-efficiency motors refer to motors with higher efficiency, and their efficiency values can reach the second level of GB18613-2012 standard. High-efficiency motors use new motor designs, new processes and new materials to improve output efficiency by reducing the loss of electromagnetic energy, thermal energy and mechanical energy. Compared with standard motors, their efficiency is increased by 4% on average.

In May 2020, China announced the latest motor energy efficiency standard "GB18613-2020 Electric Motor Energy Efficiency Limits and Energy Efficiency Grades" . The standard will be officially implemented on June 1, 2021. Energy efficiency motors below IE3 (international standard) will be forced to stop production , and the domestic motor industry will fully enter the IE3 high-efficiency era.
The new national standard also stipulates that from the date of implementation of the standard, IE3 efficiency will become China's lowest three-phase asynchronous motor energy efficiency limit value (three-level energy efficiency), and three-phase asynchronous motors (such as YE2 series motors, etc.) with energy efficiency limits lower than IE3 will not be allowed to be produced and sold, indicating that the efficiency level of China's small and medium-sized three-phase asynchronous motors has been raised to a higher level. The new national standard also lists IE4 efficiency as a second-level energy-saving evaluation value indicator.
The difference between motor energy efficiency labels after the implementation of the new national standard GB 18613-2020 is as follows:
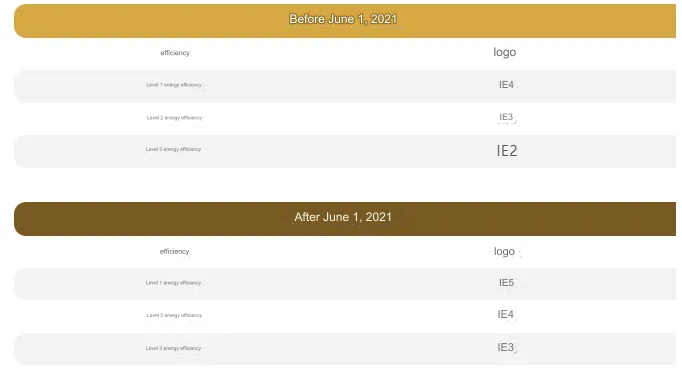
As far as motor companies are concerned, from June 1, 2021, motors that do not meet the IE3 energy efficiency limit shall not be produced or sold, and users shall not purchase them . Therefore, motor companies must be fully prepared to produce and sell IE3 and above energy efficiency motors in terms of technology, equipment, process, materials and sales.
Compared with IE2, the cost of IE3 is about 20% higher; compared with IE3, the cost of IE4 is also significantly higher. Therefore, motor companies should tap the potential in design, process and other aspects to reduce costs, on the premise that their products meet the required energy efficiency indicators. Currently, many motor companies have begun to implement intelligent manufacturing, so that motor products can achieve a higher consistency. In addition, existing motor products can be better improved in terms of process (such as processing accuracy) and equipment.



























 XINDA
XINDA