What is the relationship between the motor service coefficient and the working system?
What is the relationship between the motor service coefficient and the working system? What performance can the motor service coefficient reflect?
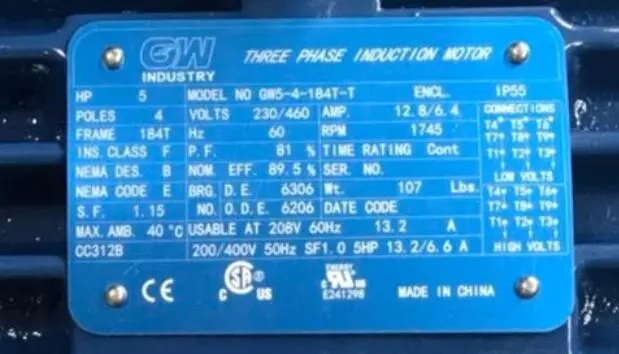


What is the relationship between the motor service coefficient and the working system? What performance can the motor service coefficient reflect?


