![]()
What types of motors are there? See uses, types, and selection considerations at once!
Electric motor, also known as electric motor or motor, is one of the indispensable and important cores of today's industrial automation. Motors have developed into various types based on their principles, structures, characteristics and application methods. This article will take an in-depth look at the different types of motors, their wide range of applications, and what you should pay attention to when purchasing.
Motor uses
Motors are widely used in various fields, from heavy industry, artificial satellites, Mars surface detectors to livelihood products, drones and toys. It can be seen that motors bring convenience and efficiency improvement to industry and daily life.
Industrial
* Cranes
*Ship vehicles
*Lifts or elevators
*Electric escalators
*Conveyor belts*
Fans
*Iron rolling doors
Civilian use
In daily life, motors can be seen everywhere. From household appliances to the drive systems of modern green vehicles, motors provide indispensable support for the operation and performance of these products.
* Electric fan
* Washing machine
* Air conditioner
* Hair dryer
* Electric toothbrush
* Vacuum cleaner
* Electric bicycle
* Drone
Common motor types
The common classification method is based on the power supplied to the motor, which is divided into DC motors and AC motors.
DC motor
The working principle of a DC motor is to use DC current to generate a magnetic field through a coil. The force generated by the magnetic field interacts with the permanent magnet to rotate the motor and change the direction of the current in a timely manner so that the rotor can continue to rotate in the same direction. DC current has a fixed current direction, a wide speed adjustment range, and is used in a wide range of products. DC motors can be used in hand tools, home appliances, industrial equipment, etc. DC motors can be divided into two types: brushed DC motors and brushless DC motors.
The brushed DC motor
is mainly composed of a stator composed of permanent magnets, a rotor composed of an axis and coils, a commutator (collector ring), and brushes (carbon brushes). The DC power supply uses a brush contact commutator to transmit current to the coil of the motor to generate a magnetic field, which interacts with the magnetic field of the permanent magnet to drive the rotor to rotate. The advantages of brushed DC motors are low price, easy to manufacture and maintain; but the disadvantages are low efficiency and high noise. The brushes wear out due to long-term contact and friction with the commutator, so they need to be replaced regularly.
Brushless DC motor
Brushless DC motor uses an electronic controller to control the current in the motor coil, and drives the motor through electrical current switching, reducing motor losses caused by friction. The advantages of brushless DC motors are higher efficiency, lower noise, and high reliability; but the disadvantages are higher prices and more complex manufacturing and maintenance.
Differences between brushed DC motors and brushless DC motors:
|
|
Brushed DC motor
|
Brushless DC motor
|
|
working principle
|
Use brushes and commutators to transfer current to the motor's coils
|
Use an electronic controller to control the current in the coil
|
|
efficiency
|
lower
|
higher
|
|
noise
|
Larger
|
smaller
|
|
cost
|
Low
|
high
|
|
Manufacturing and maintenance
|
simpler
|
more complex
|
|
Carbon brush replacement
|
regular
|
No need to replace
|
AC motor
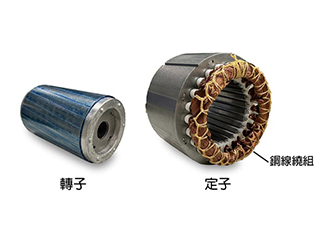
The AC motor is mainly composed of a stator winding and a rotor. When the motor is running, the stator remains stationary. When the AC current passes through the copper wire winding on the stator, a magnetic field is generated, which drives the rotor to rotate. The main categories of AC motors are:
induction motor
. Induction motor is the most common AC motor. It is characterized by simple structure, easy acquisition of manufacturing materials, relatively low manufacturing cost and wide range of applications. Induction motors can be divided into single-phase induction motors and three-phase induction motors according to different power supplies. Induction motors are commonly used in household appliances, commercial or industrial equipment, such as washing machines, refrigerators, air conditioners, rolling doors, treadmills, food machinery, packaging machinery, electric vehicles, various automation equipment, etc.
Servo motor
A servo motor is a motor that can accurately control the rotation position, speed and output torque. The servo motor system mainly consists of servo motor, position sensor and driver (controller). The driver can accurately and stably control the motor speed, rotation and output torque according to the input instructions. Therefore, for applications that require precise control of motor speed, torque, and position, servo motors need to be used, but the disadvantage is that the price is also higher. Servo motors are widely used in industrial automation control, machine tools, robots, food processing machinery, rubber and plastic machinery and other fields.
Speed-regulated motors
Single-phase induction motors can use additional speed generators and speed controllers to adjust the speed of the motor. Three-phase induction motors can change the motor speed through a frequency converter to meet the speed adjustment requirements.
Reduced motor
, also known as gear motor, uses an additional gear reducer to reduce the motor speed and increase the motor's output torque. Increasing the output torque of the motor is equivalent to increasing the load capacity of the motor, that is, improving the working capacity of the motor.
High-efficiency motor
Motor efficiency refers to the proportion of electrical energy that the motor converts into mechanical energy of rotation. The higher the efficiency of the motor, it means that it can convert more electrical energy into mechanical energy, which is equivalent to reducing the loss of electrical energy. The efficiency of a motor is usually expressed as a percentage. For example, an efficiency of 80% means that the motor can convert 80% of electrical energy into mechanical energy. Internationally, the IE level set by the International Electrotechnical Commission is usually used to represent the efficiency of the motor. IE1, IE2, IE3 and IE4 respectively represent different efficiency levels. The larger the number, the higher the efficiency and the more power it saves. Taiwan adopts CNS14400 as the motor efficiency standard.
Comparison of brushless DC motors and AC motors:
|
|
Brushed DC motor
|
Brushless DC motor
|
|
working principle
|
When the rotor coil (armature) is energized, it generates an electromagnetic field, which interacts with the permanent magnet of the stator to rotate.
|
After the stator winding coil is energized, a rotating magnetic field is generated, which attracts the rotor to rotate.
|
|
efficiency
|
lower
|
higher
|
|
cost
|
Low
|
high
|
Things to note
when selecting a motor: The selection should be based on the specific application requirements. Induction AC motors can operate in higher temperature environments, are more convenient for maintenance, and are widely used in industrial fields. Compared with AC motors, DC motors are less suitable for operation in high-temperature environments. They are simpler to control the speed and have a larger speed adjustment range. They are often used in small power tools, home appliances and toys. In addition, the following are factors that need to be considered when selecting a motor:
*Power: The power of a motor refers to the maximum energy that the motor can output when running, usually measured in watts (W). The greater the power, the greater the torque the motor can output, which means the heavier the load it can drive, and of course the greater the size and weight of the motor.
*Speed speed: refers to the number of revolutions of the motor per minute, with speed per minute (rpm) as the calculation unit. The higher the speed, the faster the motor rotates, but the smaller the torque it outputs.
*Power supply: Confirm whether the power supply used by the motor is AC or DC, and the voltage (V) and current (A) required for operation. The higher the voltage, the more power the motor can output. The greater the current, the more electricity the motor consumes.
*Efficiency: The higher the efficiency, the less power the motor consumes, but the higher the manufacturing cost and price.
*Noise: The motor will produce vibration and noise when running, and may even resonate with fixtures or other parts to produce louder sounds. Some specific application equipment or usage environments have stricter requirements and restrictions on motor operating noise.
Safety specifications or certification: Internationally, electrical, electronic and related technologies, including motors, have corresponding safety specifications to thoroughly verify, evaluate and measure the safety of products or parts. For example, CE in the European Union, UL in the United States, CSA in Canada, etc.
*Price: The price of the motor will vary depending on the above-mentioned type, power, speed, voltage, current, efficiency, noise and other factors. Appropriate products should be selected based on demand and quality.
Conclusion
An electric motor, also known as an electric motor, can convert electrical energy into kinetic energy to drive other devices or equipment. Not only are there a wide variety of motors, their performance continues to improve, but their applications have also entered our daily lives from the industrial field. When selecting motor products, in addition to paying attention to the machine equipment and environment used, you should also understand the characteristics of the motor, and then choose the appropriate product based on actual needs. Shixie has more than 30 years of experience in the manufacturing and sales of motors and reducers. Its products have obtained various international certifications, have stable quality, meet market demand, and are sold in 50 countries around the world. Welcome to contact the World Association for more information on motor products.





























 XINDA
XINDA