![]()
An electric motor (Motor) is a device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Since Faraday invented the first electric motor, this kind of equipment has become indispensable in our lives.
Nowadays, cars are rapidly changing from mechanical-based to electrical-based equipment, and motors are increasingly used in cars. Many people may not be able to guess how many motors are installed in their cars. The following introduction Will help you find the motor in your car.
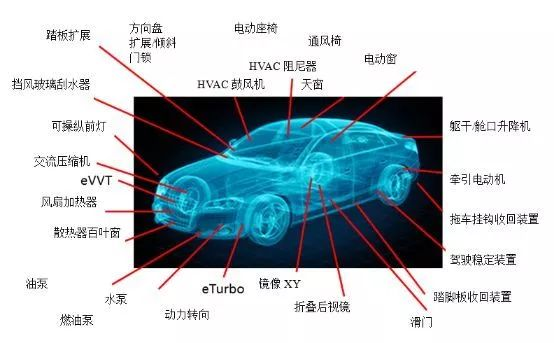
Electric motor applications in automobilesWondering where the motor is in your car, the power seat is the perfect place to find it. In economy cars, the motor generally provides fore and aft adjustment and backrest tilt functions. In high-end cars, electric motors can control height adjustment, such as seat bottom cushion tilt, lumbar support, headrest adjustment and seat cushion stability. These functions can not be separated from the motor. Other seat features that use electric motors include power seat folding and power loading of the rear seats.Windshield wipers are an example of the most common electric motor application in modern automobiles. Generally, every car has at least one wiper motor for the front wiper. Rear window wipers are becoming increasingly popular on SUVs and hatchback cars, which means that a rear wiper and corresponding motor is present on most cars. Another motor pumps washer fluid to the windshield and, in some cars, the headlights, which may have their own small wipers.Almost every car has a blower that circulates air in the heating and cooling system; many vehicles have two or more fans in the cabin. High-end vehicles also have fans installed on the seats for cushion ventilation and heat distribution.It used to be common to open and close car windows manually, but now power windows are common. Each window houses a hidden motor, including the skylight and rear window. The actuators for these windows can be as simple as relays, but safety requirements such as detecting obstacles or clamping objects will lead to the use of smarter actuators, with motion monitoring and actuation force limitations.From manual to electric, car locks have become more and more convenient. The benefits of electric control include convenience features such as remote operation, and enhanced safety and intelligence features such as automatic unlocking after a collision. Unlike power windows, power door locks must retain the option of manual operation, so this affects the design of the power door lock motor and structure.Indicators on a dashboard or cluster may have evolved into light-emitting diodes (LEDs) or other types of displays, but now every dial and gauge uses a small electric motor. In the convenience category, other motors include common functions such as side mirror folding and position adjustment, as well as more emotive applications such as convertible tops, retractable pedals and glass partitions between driver and passenger. plate.Under the hood, electric motors are becoming more common in a few other places, too. In many cases, electric motors are replacing belt-driven mechanical components. Examples include radiator fans, fuel pumps, water pumps and compressors. There are several advantages to changing these functions from belt drive to electric drive. One advantage is that drive motors using modern electronics are more energy efficient than using belts and pulleys, resulting in benefits such as improved fuel efficiency, reduced weight and lower emissions. Another advantage is that using motors rather than belts allows for more freedom in mechanical design, since where the pump and fan can be mounted does not have to be restricted by having to connect a serpentine belt to each pulley.Development trends of in-car motor technologyThe places marked in the above picture are inseparable from motors. Moreover, with the subsequent improvement of automobile electronics, the progress of autonomous driving and intelligence, motors will be used more and more in cars, and the types of motor drives will also change. Changes are happening.While most electric motors in cars previously used standard 12V automotive systems, dual-voltage 12V and 48V systems are now becoming mainstream. Dual-voltage systems can move some of the higher current loads away from the 12V battery. The advantage of using a 48V power supply is that the current is reduced by a factor of 4 for the same power, and is accompanied by a reduction in the weight of the cables and motor windings. Applications with high current loads that may be updated to 48V supplies include starter motors, turbochargers, fuel pumps, water pumps and cooling fans. Installing a 48V electrical system for these components may result in fuel consumption savings of approximately 10%.Different applications require different motors, and there are many ways to classify motors.1 .Classification according to working power supply - According to the different working power supply of the motor, it can be divided into DC motor and AC motor. AC motors are also divided into single-phase motors and three-phase motors.2. According to working principle - according to different structures and working principles, electric motors can be divided into DC motors, asynchronous motors and synchronous motors. Synchronous motors can also be divided into permanent magnet synchronous motors, reluctance synchronous motors and hysteresis motors. Asynchronous motors can be divided into induction motors and AC commutator motors.3. Classification based on starting and running modes - According to starting and running modes, motors can be divided into capacitor-started single-phase asynchronous motors, capacitor-run single-phase asynchronous motors, capacitor-started single-phase asynchronous motors and split-phase single-phase asynchronous motors.4.Classification according to use - Motors can be divided into drive motors and control motors according to their use. Driving motors are further divided into motors for power tools (including drilling, polishing, polishing, grooving, cutting, reaming and other tools), home appliances (including washing machines, electric fans, refrigerators, air conditioners, tape recorders, video recorders, DVDs, etc.) machines, vacuum cleaners, cameras, hair dryers, electric shavers, etc.) and other general small mechanical equipment (including various small machine tools, small machinery, medical equipment, electronic instruments, etc.). Control motors are divided into stepper motors and servo motors.5. Classification according to the structure of the rotor - Motors can be divided into cage induction motors (called squirrel cage asynchronous motors in the old standard) and wound rotor induction motors (called wound asynchronous motors in the old standard) according to the structure of the rotor.6. Classification based on operating speed - Motors can be divided into high-speed motors, low-speed motors, constant-speed motors, and speed-adjustable motors according to operating speed.Currently, motors in automotive body applications mostly use brushed DC motors, which is a traditional solution. Since the brushes provide the commutation function, these motors are simple and relatively cheap to drive. In some applications, brushless DC (BLDC) motors offer significant advantages in power density, reducing weight and delivering better fuel economy and lower emissions, with manufacturers in windshield wipers, cabins BLDC motors are chosen for use in heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) blowers and pumps. In these applications, where electric motors tend to operate for long periods of time rather than instantaneous operation like power windows or power seats, the simplicity and cost-effectiveness of brushed motors still have the advantage.Motors suitable for electric vehiclesThe transition from fuel vehicles to pure electric vehicles will shift the core engine of the vehicle to electric motor drive.The motor drive system is the heart of an electric vehicle. It consists of a motor, a power converter, various detection sensors and a power supply. Motors suitable for electric vehicles include: DC motors, brushless DC motors, asynchronous motors, permanent magnet synchronous motors, and switched reluctance motors.DC motor is a motor that converts DC electric energy into mechanical energy. It is widely used in electric drive because of its good speed regulation performance. It also has the characteristics of large starting torque and relatively simple control. Therefore, DC motors are suitable for any machinery that starts under heavy load or requires uniform speed adjustment, such as large reversible rolling mills, winches, electric locomotives, trams, etc.The brushless DC motor is very consistent with the load characteristics of electric vehicles. It has low-speed and high-torque characteristics and can provide large starting torque to meet the acceleration requirements of electric vehicles. At the same time, it can operate in low, medium, high and wide speed ranges. It also has high efficiency characteristics and has high efficiency under light load conditions. The disadvantage is that the motor itself is more complex than an AC motor, and the controller is more complex than a brushed DC motor.Asynchronous motor , also known as induction motor, is a device that places the rotor in a rotating magnetic field. Under the action of the rotating magnetic field, a rotational torque is obtained, so the rotor rotates. The asynchronous motor has a simple structure and is easy to manufacture and maintain. It has near-constant speed load characteristics and can meet the driving requirements of most industrial and agricultural production machinery. However, the speed of an asynchronous motor has a fixed slip rate with the synchronous speed of its rotating magnetic field, so its speed regulation is poor and it is not as economical and flexible as a DC motor. In addition, in applications with high power and low speed, asynchronous motors are not as reasonable as synchronous motors.
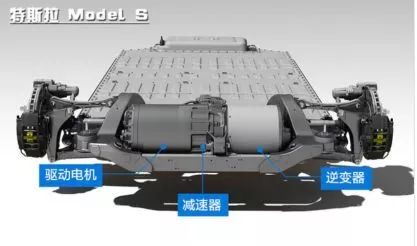
A permanent magnet synchronous motor is a synchronous motor that is excited by permanent magnets to generate a synchronous rotating magnetic field. The permanent magnets act as the rotor to generate a rotating magnetic field. The three-phase stator winding reacts through the armature under the action of the rotating magnetic field, inducing a three-phase symmetrical current. The permanent magnet motor has small size, light weight, small moment of inertia and high power density, which is suitable for electric vehicles with limited space. In addition, its torque to inertia ratio is large and the overload capacity is strong, especially at low speeds. The output torque is large, so it is suitable for computer cars. startup acceleration. Therefore, permanent magnet motors have been widely recognized by the electric vehicle industry at home and abroad and have been used in many electric vehicles.
The switched reluctance motor is a new type of speed control motor. The speed control system has the advantages of both DC and AC speed control systems. It is the latest generation stepless speed control system following the variable frequency speed control system and the brushless DC motor speed control system. It has a simple and solid structure, a wide speed regulation range, excellent speed regulation performance, high efficiency in the entire speed regulation range, and high system reliability. It mainly consists of four parts: switched reluctance motor, power converter, controller and position detector. The controller contains the power converter and control circuit, while the rotor position detector is installed at one end of the motor. Nowadays, the application and development of switched reluctance motors have made significant progress, and have been successfully used in various fields such as electric vehicle drives, general industry, household appliances, and textile machinery, with power ranging from 10W to 5MW, and maximum speeds up to 100,000 r /min.





























 XINDA
XINDA